Main Memory¶
Background¶
- Program must be brought (from disk) into memory and placed within a process for it to be run
- Main memory and registers are only storage that CPU can access directly
- Register access is done in one CPU clock or less
- Main memory can take many cycles, causing a stall
- 如果job比physical memory大
- 分治
- 同时间运行多个process
- fast switching
- 划分物理内存——partitioning
- partition requirements
- protection: keep processes from smashing each other
- Fast execution: memory accesses can’t be slowed by protection mechanisms
-
Fast context switch: can’t take forever to setup mapping of addresses
-
加载一个进程
- relocate all addresses relative to start of partition
- 一旦进程开启,由于内存内有很多指针,移动内存是不现实的


- problem: 当上述情况后有一个进程4进入,但需要的空间大于单个empty部分,但小于所有empty的和
- solution: use logical address instead of physical address, define it as the offset within the partition
- 这样就可以move process了
Partition¶
Simplest Implementation¶
-
Base and Limit registers
-
每个进程都有自己的base和limit,每次进程切换时,OS 都会将 base 和 limit 寄存器的值更新为当前进程的值。若输入地址不超过limit,则会加上base后访问,否则segment fault
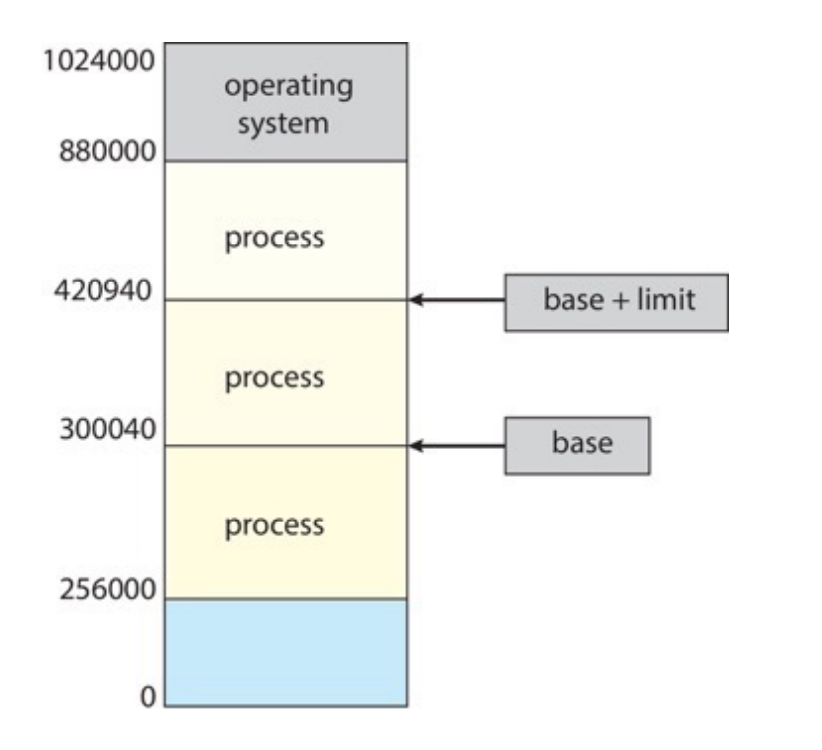
- Hardware Address Protection

-
Advantages
-
Built-in protection provided by Limit
- No physical protection per page or block
-
Fast execution
- Addition and limit check at hardware speeds within each instruction
-
Fast context switch
- Need only change base and limit registers
-
No relocation of program addresses at load time
- All addresses relative to zero
-
Partition can be suspended and moved at any time
- Process is unaware of change
修改 base 即可移动进程,进程是意识不到的。
- Expensive for large processes
移动进程需要改 base,还要把旧的内容全部改到新的位置,耗时。
Memory Allocation Strategies¶
- fixed partitions or variable partitions
- 取决于长度是否会发生变化
Fixed partitions¶
- divide memory into equal sized pieces
- degree of multiprogramming = number of partitions
- 每一个partition可以且只可以放一个进程,剩下的空间就会被浪费 Big waste of memory
- 如果单个process超过partition大小,只能采取分治拆成更小的process
- size 要切多大?如果切的太小,可能有大进程无法加载进来;如果切的太大,会有内部碎片

Variable partitions¶
-
Hole: block of available memory, holes of various size scattered throughout memory
-
长度不一致,按需划分。即要给一个进程分配空间时,我们找到比他大的最小的 partition (best fit),然后把他放进去。
- first-fit: allocate from the first block that is big enough
- best-fit: allocate from the smallest block that is big enough
-
worst-fit: allocate from the largest hole
-
Memory is dynamically divided into partitions based on process needs
-
More complex management problem
- Need data structures to track free and used memory
- New process allocated memory from hole large enough to fit it
-
Problem – External Fragmentation
-
Unused memory between partitions too small to be used by any processes
在 partition 之外的空闲空间太小,无法被任何进程使用。
-
the request cannot be fulfilled because the free memory is not contiguous.
-
can be reduced by compaction
- 将所有free memory连续放置
- program needs to be relocatable at runtime
- performance overhead, timing to do this operation
Segmentation¶
readelf可以打印所有的section header一个elf至少需要5个partition,.text, .data, .bss, heap, stack
- 利用partition的概念实现了segmentation的机制
-
认为 text、data、stack 是多个区域,每个区域就可以用一个 partition 来代表它
-
Logical address consists of a pair:
-
<segment-number, offset>segment-number 表示属于第几组。
-
Offset is the address offset within the segment.
-
现在硬件可以support八千多个segment
-
Segment table where each entry has:
- Base: starting physical address
- Limit: length of segment
-
一个segment只能有一种权限
-
Segment Lookup

- 仍然存在external fragmentation
- 早期Intel在x86实现了segmentation,一直保留到现在
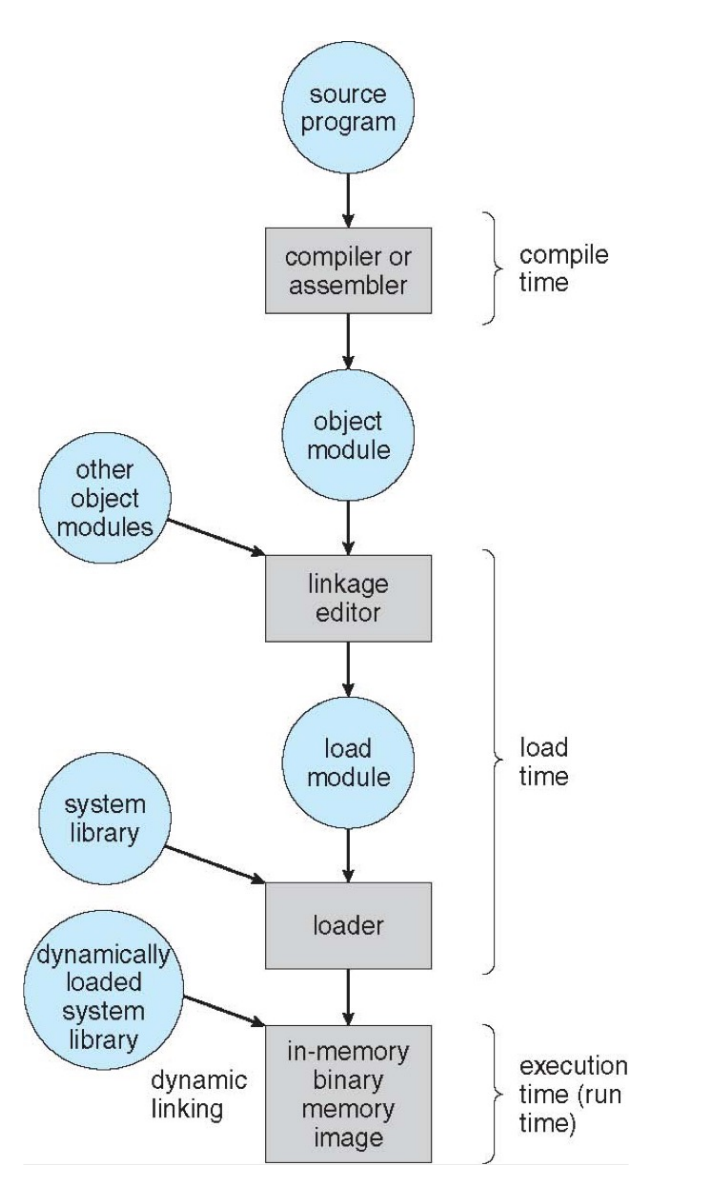
Address Binding¶
Address binding of instructions and data to memory addresses can happen at three different stages.
- Compile time: If memory location known a priori, absolute code can be generated; must recompile code if starting location changes.
- Load time: Must generate relocatable code if memory location is not known at compile time.
- Execution time: Binding delayed until run time if the process can be moved during its execution from one memory segment to another.
- Need hardware support
Logical vs. Physical Address¶
-
直接使用物理地址无法进行内存管理,因此需要使用逻辑地址
-
逻辑地址由CPU生成,也被叫做virtual address
- 逻辑地址需要映射到物理地址来存储,逻辑地址只存在地址,而没有实际存储的space
- 逻辑地址对应逻辑地址空间(Logical Address Space),物理地址对应物理地址空间(Physical Address Space)
Memory-Management Unit¶
- map logical address to physical address
- CPU uses logical addresses
- Memory unit uses physical address
- Like speaking “different languages”, MMU does the translation
做地址的transition
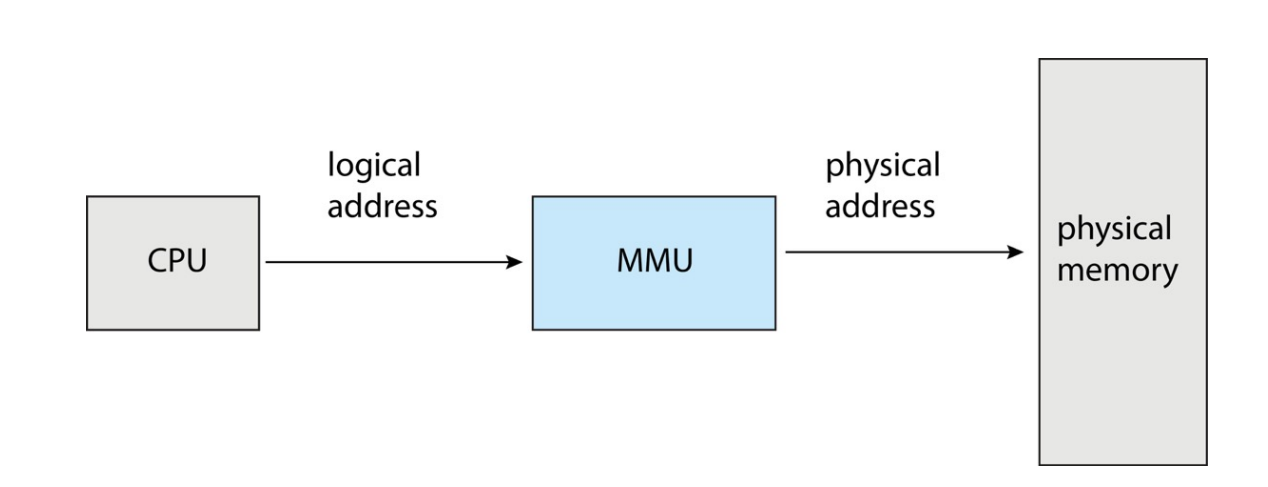
The base register now called relocation register
Paging¶
- Basic idea: contiguous -> noncontiguous
-
Physical address space of a process can be noncontiguous; process is allocated physical memory whenever the latter is available. Fixed 和 Variable 划分都是物理连续的分配,Paging 是把所有内存都变成不连续的,这样空闲的内存不管在哪,都可以分配给进程,避免了外部碎片。
-
Basic methods
-
divide physical address into fixed-sized blocks called frames (帧)
- Size is power of 2, usually 4KB.
-
Divide logical address into blocks of same size called pages(页)
-
注意以上两个名词的对应关系
-
need to keep track of all free frames
-
To run a program of size N pages, need to find N free frames and load program.
把 N 个帧映射到 N 个页。(页和帧是一样大的)
-
Set up a mapping to translate logical to physical addresses.
- This mapping is called page table.
存储帧到页的映射,这个数据结构叫页表。
-
Paging由于使用fixed,因此没有external fragmentation,只有internal fragmentation
-
只可能在最后一页存在fragmentation,因为前面的页都填满了才可能用到下一页
-
因此:平均internal fragmentation是½的frame size
-
页小,碎片少,但分的更碎,page table更大;页大,碎片更大但映射更少,页表更小。现在页逐渐更大,因为内存不值钱了,mac已经64KB了
Page Table¶
- frame table: 一个bitmap,记录哪些frame空闲
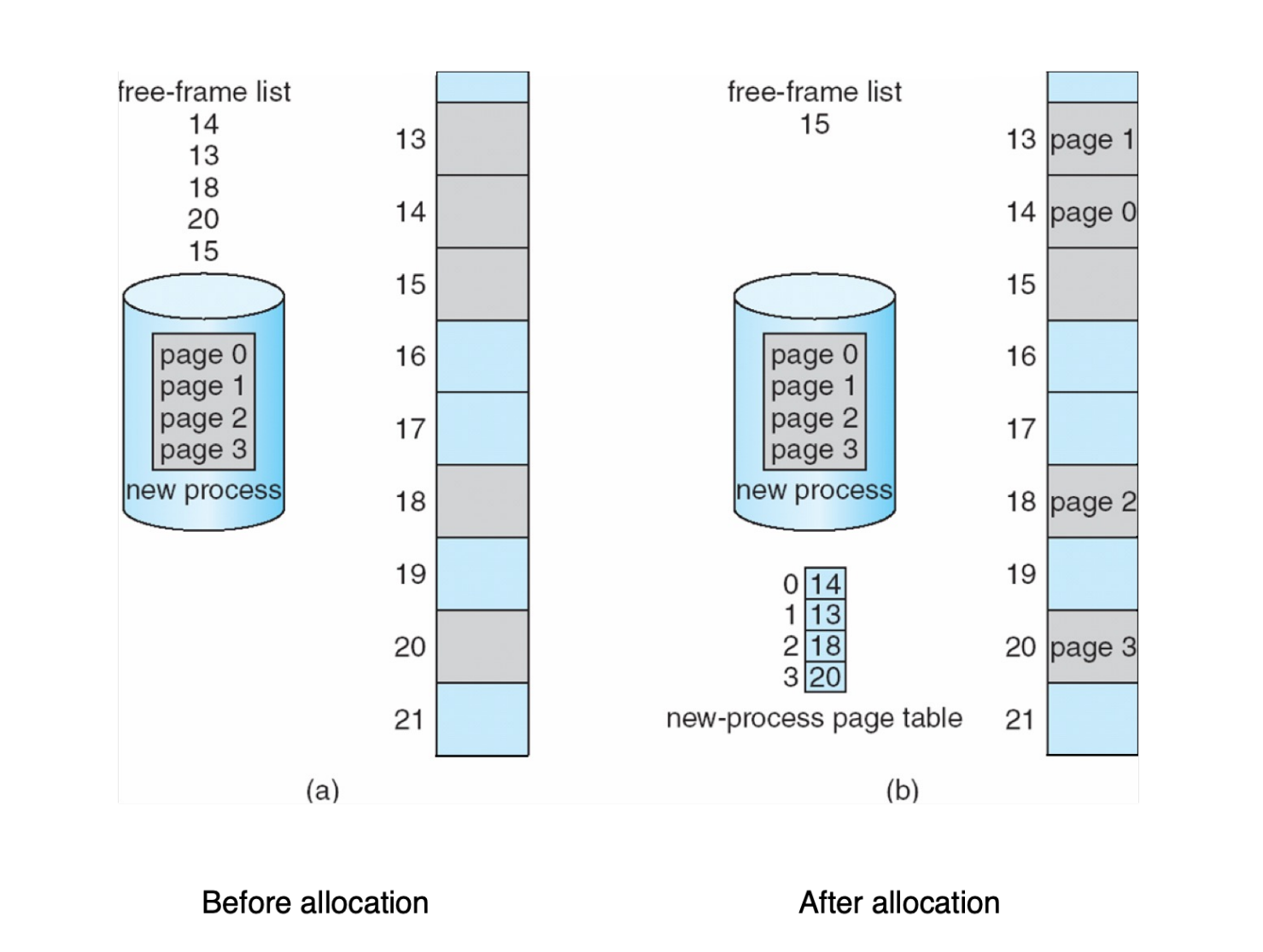
- page table存的是物理地址的帧号,页号就是index
Address Translation¶
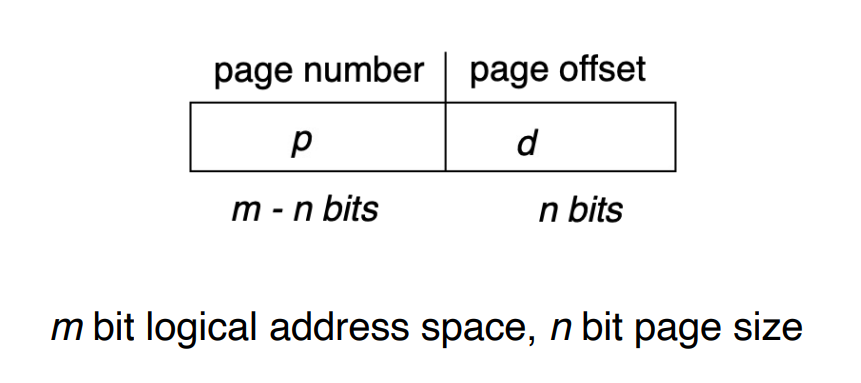
A logical address is divided into:
- page number (p)
- used as an index into a page table
- page table entry contains the corresponding physical frame number
- page offset (d)
- offset within the page/frame
- combined with frame number to get the physical address
- 把p对应到page table找到对应物理帧号,加上offset得到物理地址

Paging Hardware¶
Simplest Case: 使用register储存,速度快,但缺点是register数量有限,table size会很小,上下文切换需要存储和重新加载这些寄存器
One big page table maps logical address to physical address
-
the page table should be kept in main memory
-
page-table base register (PTBR) points to the page table
PTBR 指向页表的起始地址。(RISC-V 上叫 SATP,ARM 上叫 TTBR,x86 上叫 CR3)
- page-table length register (PTLR) indicates the size of the page table
这样之后每次取数据/指令都需要两次memory access,第一次把页表读出来,第二次再根据页表去读数据
- Solution: 加一层cache
CPU can cache the translation to avoid one memory access
TLB(Translation look-aside buffer)¶
- TLB hit: if page number is in the TLB, no need to access the page table.
- TLB miss: if page number is not in the TLB, need to replace one TLB entry.
- TLB usually use a fast-lookup hardware cache called associative memory
- TLB is usually small, 64 to 1024 entries
每个进程有自己的页表,所以我们 context switch 时也要切换页表,要把 TLB 清空。
TLB must be consistent with page table
-
Option I: Flush TLB at every context switch, or,
-
Option II: Tag TLB entries with address-space identifier (ASID) that uniquely identifies a process.
通用的全局 entries 不刷掉,把进程独有的 entries 刷掉。
- TLB and OS
- MIPS: 操作系统层面处理TLB miss
- X86:硬件处理

-
A TLB entry match occurs when the following conditions are met:
-
Its VA, moderated by the page size such as the VA bits[47:12], matches that of the requested address
-
The memory space matches the memory space state of the requests
-
The ASID matches the current ASID held in the CONTEXTIDR, TTBR0, or TTBR1 register or the entry is marked global
-
The VMID matches the current VMID held in the VTTBR register
Effective Access Time¶
-
Hit ratio – percentage of times that a page number is found in the TLB
-
Effective Access Time (EAT)
Example
Memory Protection¶

- Each page table entry has a present (aka. valid) bit
-
present: the page has a valid physical frame, thus can be accessed
-
Each page table entry contains some protection bits
-
kernel/user, read/write, execution?, kernel-execution?
-
Any violations of memory protection result in a trap to the kernel
-
XN: protecting code
-
Segregate areas of memory for use by either storage of processor instructions (code) or for storage of data.
代码无论在 user 还是 kernel 状态下都不能执行。
e.g. Intel: XD(execute disable), AMD: EVP (enhanced virus protection), ARM: XN (execute never)
-
PXN: Privileged Execute Never
-
A Permission fault is generated if the processor is executing at EL1(kernel) and attempts to execute an instruction fetched from the corresponding memory region when this PXN bit is 1 (usually user space memory)
在特权模式下不能执行。
Page Sharing¶
Paging allows to share memory between processes
- shared memory can be used for inter-process communication
-
shared libraries
-
Reentrant code: non-self-modifying code: never changes between execution

Structure of Page Table¶
Page table must be physically contiguous.
如果只有一级的页表,那么页表所占用的内存很大。e.g. 32-bit logical address space and 4KB page size. page table would have 1 million entries (\(2^{32}\) / \(2^{12}\)). If each entry is 4 bytes -> 4 MB of memory for page table alone.
我们需要有方法压缩页表。
- Break up the logical address space into multiple-level of page tables. e.g. two-level page table
- First-level page table contains the frame# for second-level page tables.
Two-Level Paging¶

最坏情况下,如果只访问第一个页和最后一页,那么只用一级页表需要 1K 个页用来放页表(这个页表有 \(2^{20}\) 个条目),但是对于二级页表就只需要 3 个页表(1 个一级和 2 个二级页表),即 3 个页来放页表。 4MB -> 12KB
多级页表只有当需要时才会创建页表,从而做到省空间 hold
A logical address is divided into:
- a page directory number (first level page table)
- a page table number (\(2^{nd}\) level page table)
- a page offset

Example: 2-level paging in 32-bit Intel CPUs
• 32-bit address space, 4KB page size
• 10-bit page directory number, 10-bit page table number
• each page table entry is 4 bytes, one frame contains 1024 entries (\(2^{10}\))
Page Table in Linux
页表里存的都是物理地址(物理页号)
64-bit Logical Address Space¶
-
页表仍然4KB,entry变成8B,因此page table每个可以存储512个entry,即\(2^9\)
-
由于这时候离用完64位还差很多,因此我们可以不断添加level
-
usually not support full 64-bit virtual address space
• AMD-64 supports 48-bit
• ARM64 supports 39-bit, 48-bit
Implementation
ARM64: 39=9+9+9+12


- PTE: 页表项(page table entry)
- PGD(Page Global Directory)
- P4D 没名字起了
- PUD(Page Upper Directory)
- PMD(Page Middle Directory)
页表为什么可以省内存,如果次级页表对应的页都没有被使用,就不需要分配这个页表。
Hashed Page Tables¶
In hashed page table, virtual page# is hashed into a frame#.
-
the page table contains a chain of elements hashing to the same location
-
Each element contains: page#, frame#, and a pointer to the next element (resolving conflict)
哈希页表的每一个条目除了 page number 和 frame number 以外,还有一个指向有同一哈希值的下一个页表项的指针。这个结构与一般的哈希表是一致的。
用链表处理冲突
-
Hashed page table can be used in address spaces > 32 bits
-
Clustered page tables
-
Each entry refers to several pages
Inverted Page Table¶
- tracks allocation of physical frame to a process
- page table的每个entry存process id和page#

- 整个系统只有一个页表,并且每个物理内存的 frame 只有一条相应的条目 (对应的index)
- 每次要遍历整个页表,效率低下
- how to implement shared memory?
- a physical frame can only be mapped into one process!
- Because one physical memory page cannot have multiple virtual page entry!
Swapping¶
- Swapping extends physical memory with backing disks
- A process can be swapped temporarily out of memory to a backing store
- Backing store is usually a (fast) disk
- The process will be brought back into memory for continued execution
- Context switch time can become very high due to swapping
- If the next process to be run is not in memory, need to swap it in
- Disk I/O has high latency

Swapping with Paging¶
- swap pages instead of entire process

Swapping on Mobile Systems¶
-
一般不支持,比如U盘swapping有次数限制
-
Instead use other methods to free memory if low
- iOS asks apps to voluntarily relinquish allocated memory
- Read-only data thrown out and reloaded from flash if needed
- Failure to free can result in termination
- Android terminates apps if low free memory, but first writes application state to flash for fast restart
Virtual address format¶
- 48-bit VA with 4KB page

- 48-bit VA with 64KB page




