Deadlock¶
Deadlock problem¶
- Deadlock: a set of blocked processes each holding a resource and waiting to acquire a resource held by another process in the set.
-
可以用resource allocation graph表示,有环则死锁
-
Four conditions of deadlock
-
Mutual exclusion: a resource can only be used by one process at a time.
互斥,资源在一个时间只能被一个进程使用。
-
Hold and wait: a process holding at least one resource is waiting to acquire additional resources held by other processes.
已经有了一些资源,同时想要更多资源。
-
No preemption: a resource can be released only voluntarily by the process holding it, after it has completed its task.
已经获得的资源不能被抢占,只能由自己释放。
-
Circular wait: there exists a set of waiting processes \(\{P_1,P_2,\dots,P_n\}\)
- \(P_0\) is waiting for a resource that is held by \(P_1\)
- \(P_1\) is waiting for a resource that is held by \(P_2\) ...
- \(P_{n-1}\) is waiting for a resource that is held by \(P_{n}\)
- \(P_{n}\) is waiting for a resource that is held by \(P_0\)
- resource allocation graph
-
Two types of nodes:
-
\(P = \{P_1, P_2, \ldots, P_n\}\), the set of all the processes in the system
-
\(R = \{R_1, R_2, \ldots,R_m\}\), the set of all resource types in the system
-
Two types of edges:
-
request edge: directed edge \(P_i \rightarrow R_j\)
进程需要这个资源。
-
assignment edge: directed edge \(R_j \rightarrow P_i\)
资源已经分配给这个进程。

这里没有死锁,P3 先执行,随后释放 R3,再执行 P2,最后 P1。
有死锁,存在circular wait
无死锁
- Basic Facts
- If graph contains no cycles ➠ no deadlock
- If graph contains a cycle
- if only one instance per resource type, ➠ deadlock
- if several instances per resource type ➠ possibility of deadlock
Handling deadlocks¶
-
Ensure that the system will never enter a deadlock state
-
Prevention
-
Avoidance
-
Allow the system to enter a deadlock state and then recover - database
-
Deadlock detection and recovery
-
Ignore the problem and pretend deadlocks never occur in the system
现在操作系统都是这样做,假装无事发生,因为无法提前预测死锁的发生。
Deadlock Prevention¶
-
mutual exclusion: sharable 的可以,non-sharable 的没办法。
-
hold and wait: whenever a process requests a resource, it doesn’t hold any other resources
-
require process to request all its resources before it begins execution
-
allow process to request resources only when the process has none
申请资源时不能有其他资源,要一次性申请所有需要的资源
-
no preemption 用的不多
-
circular wait
-
impose a total ordering of all resource types
给锁一个优先级排序,取锁的时候要求从高往低取锁。
-
require that each process requests resources in an increasing order
-
Many operating systems adopt this strategy for some locks.
Deadlock Avoidance¶
在分配资源之前,先判断是否会死锁,如果会死锁就不分配。
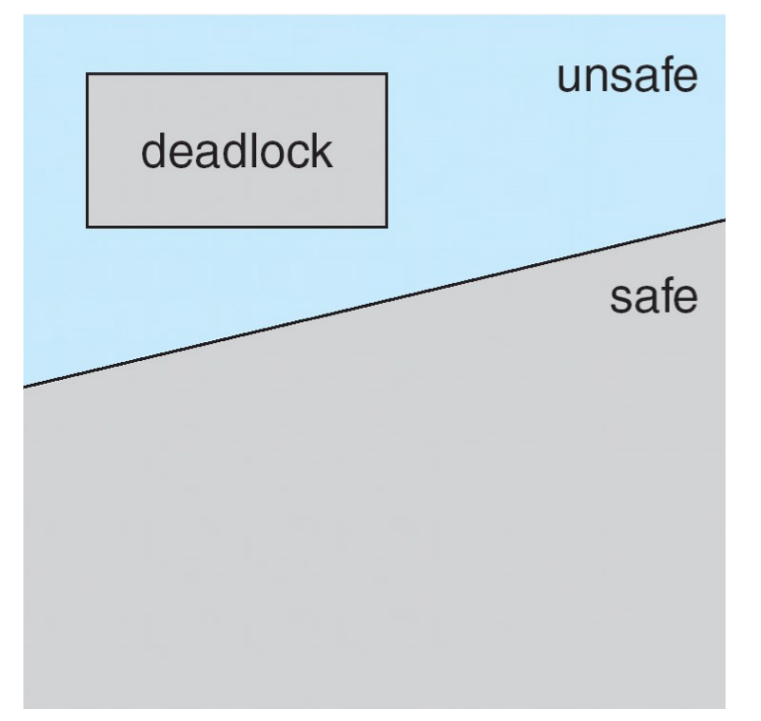
Safe State¶
-
there exists a sequence \(<P_1, P_2, \ldots, P_m>\) of all processes in the system
-
for each \(P_i\), resources that \(P_i\) can still request can be satisfied by currently available resources + resources held by all the \(P_j\).
序列里的每一个进程都可以被满足。(空闲的资源和之前的进程释放的资源)
Safe state can guarantee no deadlock.
- if \(P_i\)’s resource needs are not immediately available:
- wait until all \(P_j\) have finished
- when \(P_j\) has finished, \(P_i\) can obtain needed resources,
- when \(P_i\) terminates, \(P_{i+1}\) can obtain its needed resources, and so on.
Note
- If a system is in safe state \(\rightarrow\) no deadlocks
- If a system is in unsafe state \(\rightarrow\) possibility of deadlock
- Deadlock avoidance \(\rightarrow\) ensure a system never enters an unsafe state
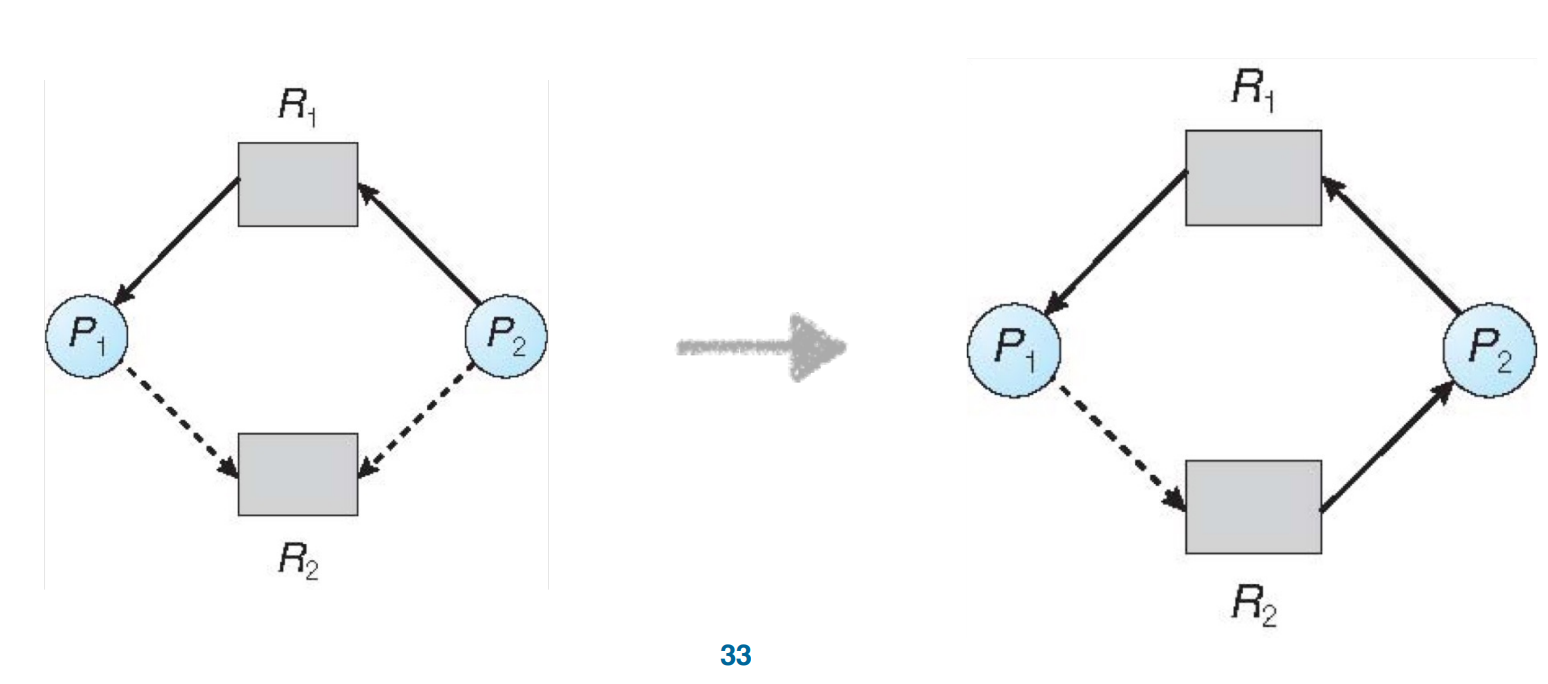
Single-instance Deadlock Avoidance¶
-
相比之前的resource allocation graph,多了一个claim edge,即声明某个进程需要调用某个资源,但还没request,使用dashed line表示,需要事先声明。
-
Transitions in between edges
-
claim edge converts to request edge when a process requests a resource
-
request edge converts to an assignment edge when the resource is allocated to the process
-
assignment edge reconverts to a claim edge when a resource is released by a process
-
Algorithm
-
Suppose that process \(P_i\) requests a resource \(R_j\)
- The request can be granted only if:
- converting the request edge to an assignment edge does not result in the formation of a cycle.
- no cycle \(\rightarrow\) safe state
比如这里分配之后就有一个环,no safe state.
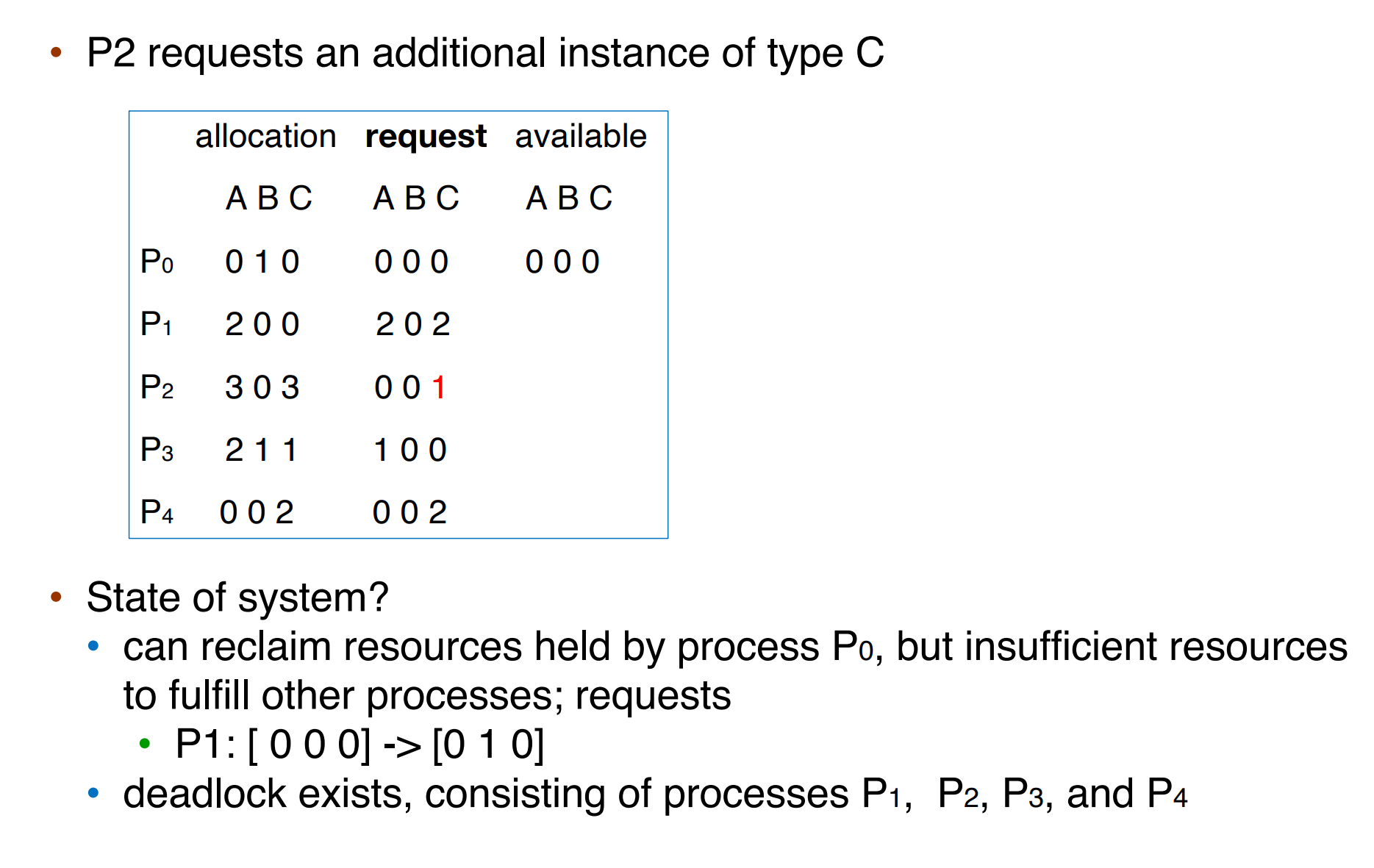
Banker's Algorithms¶
我们通过 available(当前还没有被分配的空闲资源), max(进程所需要的资源), allocation(已经分配的资源), need(还需要分配多少资源) 这四个矩阵刻画一个时间内各个进程对各种资源的持有和需求情况。
选取一个 need(的每一项都对应地)小于 available(的对应项)的进程,其运行完后会将 allocation 释放回 work(前面的进程执行完毕后,空闲的资源),以此类推。
- 第一个最后可以完成
- 第二个不行
Deadlock Detection¶
Single Instance Resources¶
使用wait-for graph
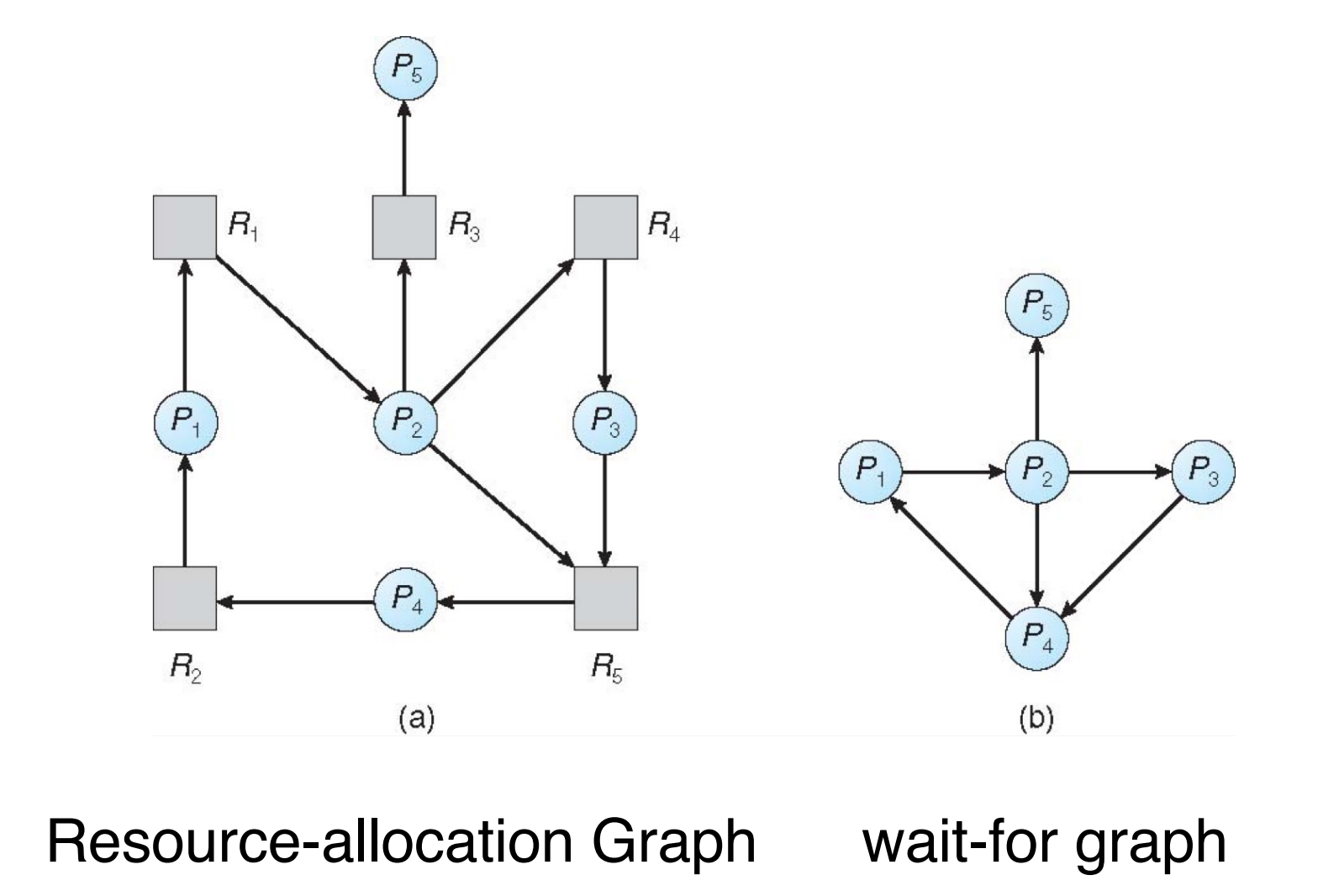
Periodically invoke an algorithm that searches for a cycle in the graph
- if there is a cycle, there exists a deadlock
有环就有 deadlock。
-
an algorithm to detect a cycle in a graph requires an order of \(n^2\) operations,
-
where \(n\) is the number of vertices in the graph.
- 算法:从每个点出发两条路,一条每次走一个node,另一条每次走两个node,两条路若在某时刻终点重合,则有环
Multi-Instance Resources¶
类似银行家算法。如果找不到任何安全序列,则说明系统处于死锁状态。
Deadlock Recovery¶
Options
- Terminate deadlocked processes options
- abort all deadlocked processes
- abort one process at a time until the deadlock cycle is eliminated
- Resource preemption
- select a victim
- rollback
- starvation