Mass-Storage Structure¶
Disk Structure¶
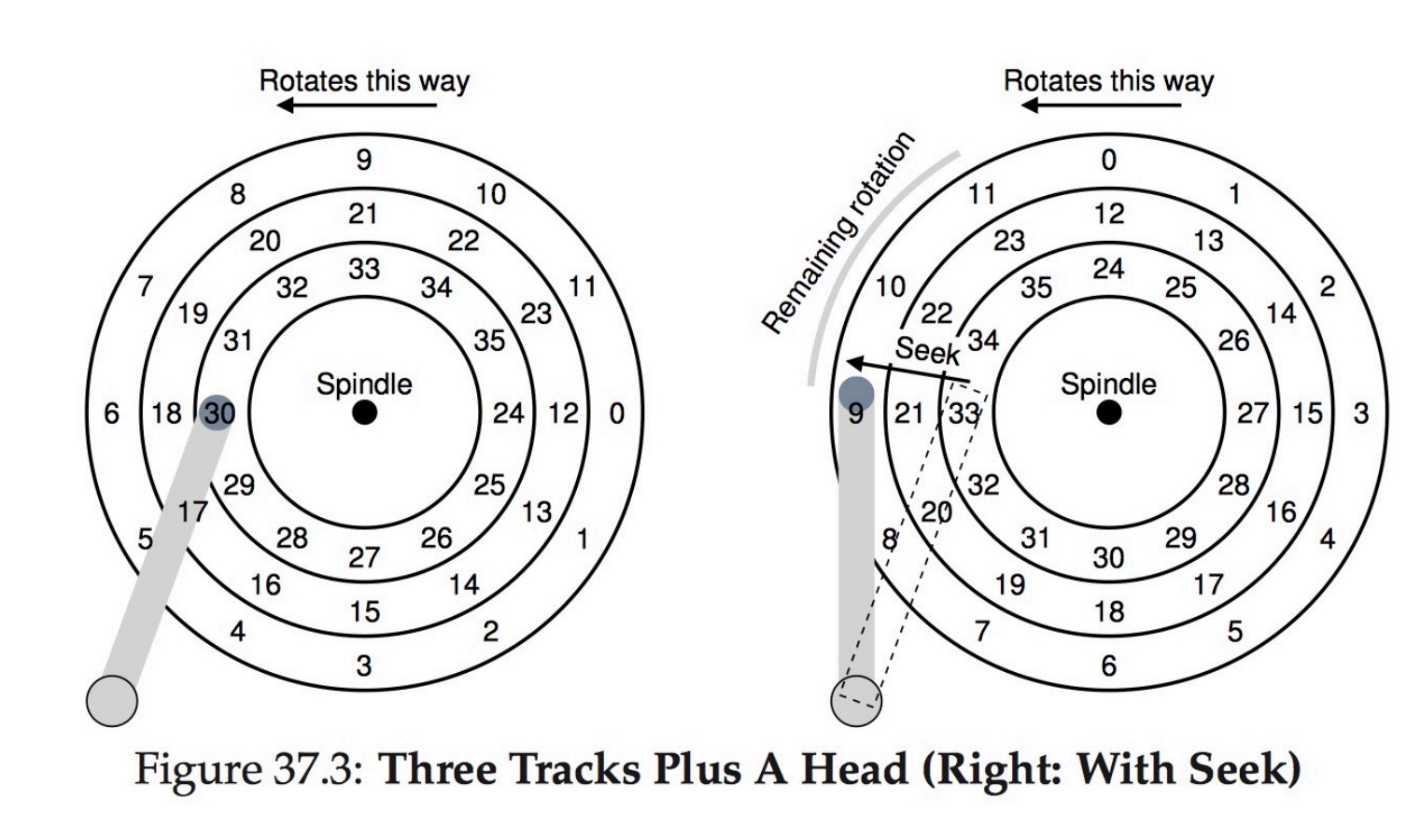
- Positioning time(random-access time) is time to move disk arm to desired sector
- seek time: move disk to the target cylinder
-
rotational latency: for the target sector to rotate under the disk head
-
Performance
- transfer rate: theoretical 6 Gb/sec; effective (real) about 1Gb/sec
- seek time from 3ms to 12ms (9ms common for desktop drives)
- latency based on spindle speed: 1/rpm * 60
- average latency = ½ latency
主要慢在 seek 和 rotation 部分。
Disk Scheduling¶
- Disk scheduling chooses which pending disk request to service next
- Concurrent sources of disk I/O requests include OS, system/user processes
- Idle disk can immediately work on a request, otherwise OS queues requests
- OS maintains a queue of requests, per disk or device
- Optimization algorithms only make sense when a queue exists
-
以前 OS 会负责调度,现在由 firmware 负责(disk controller)。
-
用于minimize seek time
- rotational latency is difficult for OS to calculate
FCFS¶
First-come first-served, simplest scheduling algorithm.
- 640 cylinders for the example below
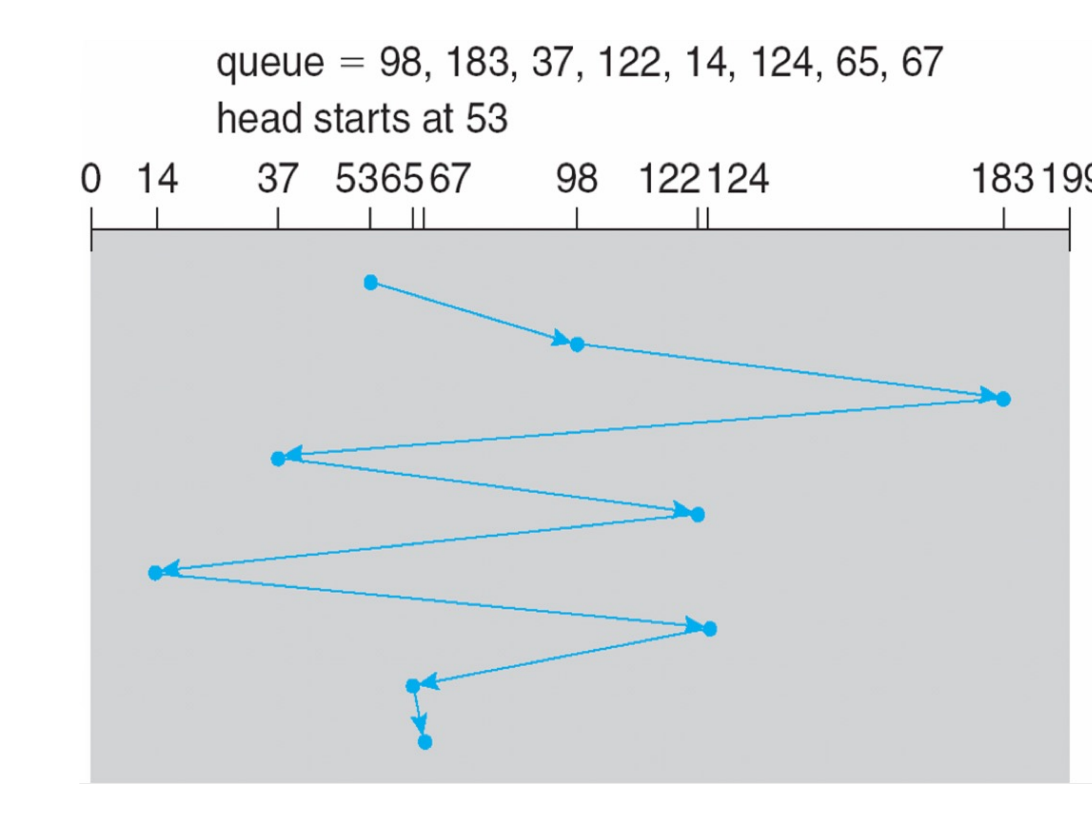
- Advantage:
- Every request gets a fair chance
- No indefinite postponement
- Disadvantages:
- Does not try to optimize seek time
- May not provide the best possible service
SSTF¶
shortest seek time first,不一定optimal,可能发生starvation

- Advantages:
- Average Response Time decreases
- Throughput increases
- Disadvantages
- Overhead to calculate seek time in advance
- Starvation may exist
- High variance: favors only some requests
SCAN¶
也叫 elevator 电梯算法,先扫到一头,再往另一头扫,如果遇到 request 就读取。
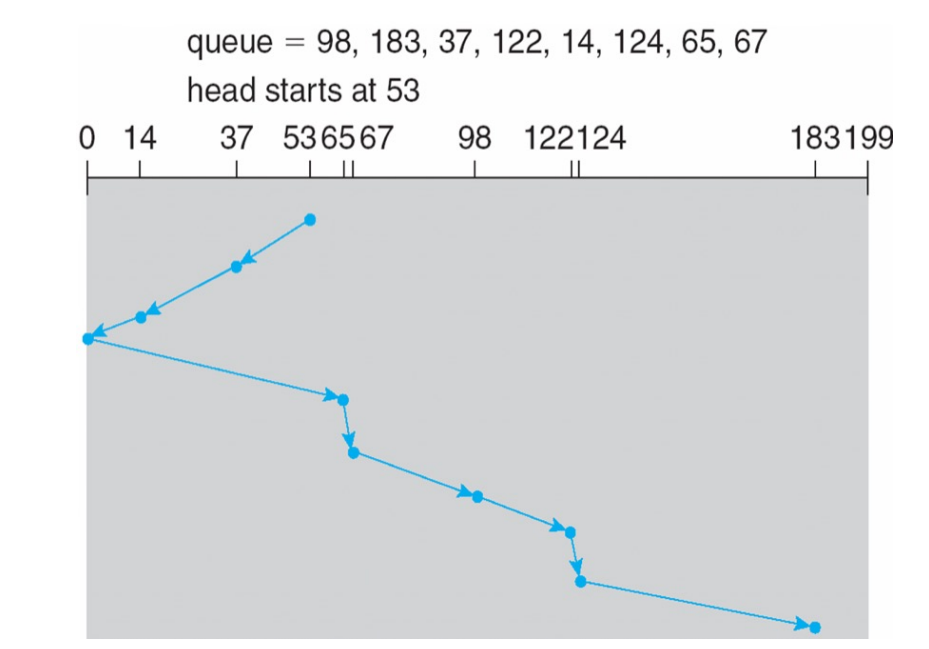
-
Advantages:
-
Average Response Time
- High Throughput
-
Low variance of response time
-
Disadvantages:
-
Long waiting time for requests for locations just visited by disk arm
如果刚好错过电梯,就要等电梯触底再上来,等待时间很长。
C-SCAN(Circular-SCAN) is designed to provides a more uniform wait time. 只做单向的扫,到达一端时立刻回到开头,随后从底往上扫,这样最多只用等待一圈。
LOOK¶
在 SCAN / C-SCAN 的基础上,只走到一端最后一个任务(look 是否有请求)而不走到 disk 的头。
LOOK is a version of SCAN, C-LOOK is a version of C-SCAN.

- Advantage:
- Prevents the extra delay which occurred due to unnecessary traversal to the end of the disk.
Selecting Disk-Scheduling Algorithm¶
- Disk scheduling performance depends on the # and types of requests
- Disk-scheduling should be written as a separate, replaceable, module
- SSTF is common and is a reasonable choice for the default algorithm
- LOOK and C-LOOK perform better for systems that have heavy I/O load 如数据库
- Disk performance can be influenced by file-allocation and metadata layout
- File systems spend great deal of efforts to increase spatial locality
依赖于请求的模式,而请求本身又依赖于文件分配策略。文件系统如果注重空间局部性,能够提供很好的表现提升。
如果 I/O 比较少,FCFS 和 SSTF 即可。如果是大型的服务器或者数据库,一般使用 C-LOOK。如果是 SSD(不用 seek),一般使用 FCFS。
Nonvolatile Memory Devices¶
If disk-drive like, then called solid-state disks (SSDs). 固态硬盘
Can be more reliable than HDDs,
与磁盘相比,寿命短,容量小,速度快(Bus 慢,需要直接连到 PCIE 上)。没有 arm 也不需要转,因此不存在 seek time 和 rotational latency.
-
Read and written in “page” increments (think sector) but can’t overwrite in place.
-
Must first be erased, and erases happen in larger “block”
-
Assume block size: 64k
-
Can only be erased a limited number of times before worn out – ~ 100,000
寿命短,里面是用门电路实现。充放电(擦写)门会被击穿,就无法区分 0/1 了。
-
Life span measured in drive writes per day(DWPD)
Each cell has lifespan, so need to write equally to all cells.
-
NAND Flash Controller Algorithms
-
maintain flash translation layer(FTL) table
-
allocate over-provisioning to provide working space for GC
避免有某一块区域被频繁使用,平衡访问次数
Magnetic Tape¶
磁带,容量很大,但是很慢。因为需要倒带,一般都做顺序访问而不是随机访问。现在主要用来做备份。
便宜 需要先格式化
data stored on the tape are relatively permanent.
Disk Management¶
使用这些介质(磁盘、固态硬盘、磁带)的时候,需要先格式化。
Physical formatting: divide disk into sectors for controller to read/write. 即把介质上分好不同的部分。
OS records its own data structures on the disk
- partition disk into groups of cylinders, each treated as a logical disk.
- logical formatting partitions to make a file system on it.
Boot block can point to boot volume or boot loader set of blocks that contain enough code to know how to load the kernel from the file system
- Boot block initializes system
- The bootstrap is stored in ROM, firmware
- Bootstrap loader program stored in boot blocks of boot partition
RAMDisk: in-memory file system
Swap Space Management¶
Used for moving entire processes (swapping), or pages (paging), from DRAM to secondary storage when DRAM not large enough for all processes
Data structures for swapping on Linux systems:
- 0 means not used
- 3 means mapped to 3 proc
Disk Attachment¶
host-attached storage¶
-
hard disk, RAID arrays, CD, DVD, tape
-
attach directly via an I/O bus

network-attached storage¶
-
NAS is storage made available over a network instead of a local bus
-
client can remotely attach to file systems on the server
Storage Area Network¶
-
SAN is a private network connecting servers and storage unit
-
SAN uses high speed interconnection and efficient protocols

RAID¶
Redundant Array of Independent Disks
Disks are unreliable, slow, but cheap. So use redundancy to increase reliability and speed
- Data Mirroring: Keep the same data on multiple disks
- Data Striping: Keep data split across multiple disks to allow parallel reads
- Error-Code Correcting (ECC) - Parity Bits: Keep information from which to reconstruct lost bits due to a drive failing
RAID 0¶
没有 redundancy,什么也不做,把数据分散在不同的磁盘。
Accessing a single strip is not faster
Improves performance, but not reliability.
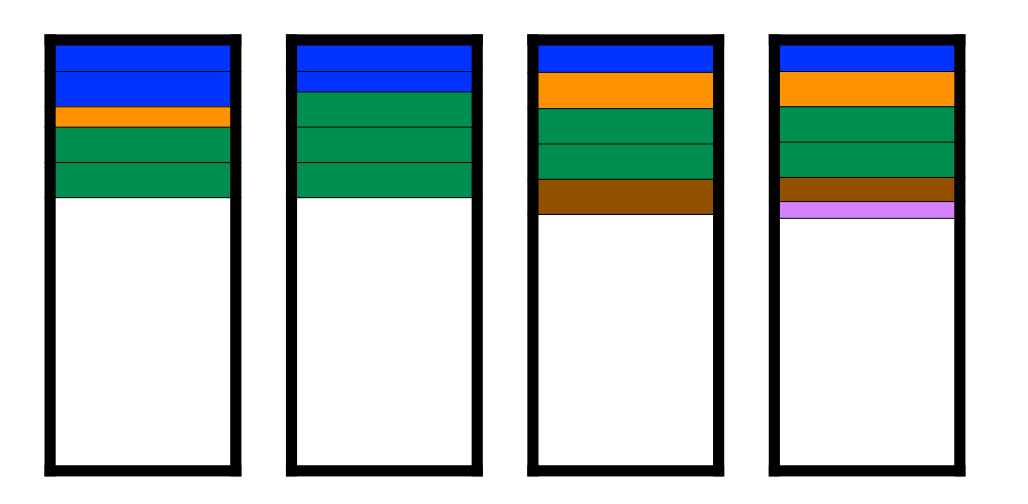
Example * Fixed strip size * 5 files of various sizes * 4 disks
RAID 1¶
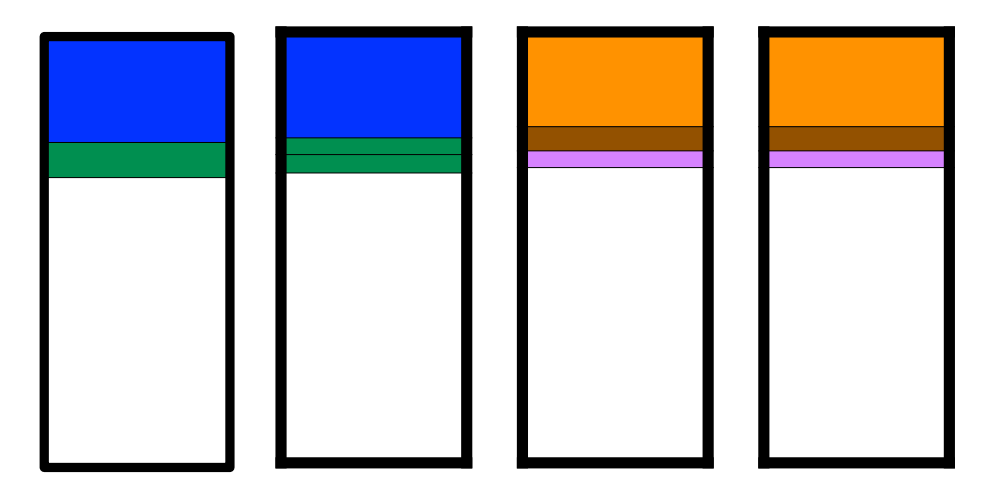
也被称为 mirroring,存在两个磁盘,一个是主磁盘,一个是备份磁盘。主磁盘写入数据后,备份磁盘也写入相同的数据。
Example
- 5 files of various sizes
- 4 disks
Reliability is ensured unless you have (extremely unlikely) simultaneous failures, performance can be boosted by reading from the disk with the fastest seek time.
但是浪费了一半的磁盘。
RAID 2¶
stripes data at the bit-level; uses Hamming code for error correction (not used).
没有被实际应用,因为粒度太小,现在无法单独读出来一个比特,至少读出一个字节。

RAID 3¶
Data is striped across multiple disks, with one dedicated parity disk that stores the parity information for all the data disks.
纠错码就在一个磁盘里。
Time to recovery is long (a bunch of XOR’s)

RAID 4,5,6¶
- RAID 4: Basically like RAID 3, but interleaving it with strips (blocks)
用块来做 strip,纠错码单独存在一个盘里。这个纠错盘一直会被读写,很有可能先损坏。
- RAID 5: Like RAID 4, but parity is spread all over the disks as opposed to having just one parity disk.
parity bit 被分散地存到了不同的磁盘里。相比于 RAID 4,每个盘的读写比较均衡。
- RAID 6: extends RAID 5 by adding an additional parity block.
又加了一个 parity bit,也是分散存储。

RAID and File Systems¶
RAID 只检测磁盘失效,并不知道对应的是哪个文件失效。
It does not prevent or detect data corruption or other errors
ZFS adds checksums to all FS data and metadata.
这样可以检验磁盘是否写错。