OS Structures¶
Various ways to structure ones
- Simple structure - MS-DOS
- Monolithic - UNIX
- Layered - an abstraction
- Microkernel - Mach
A View of Operating System Services¶
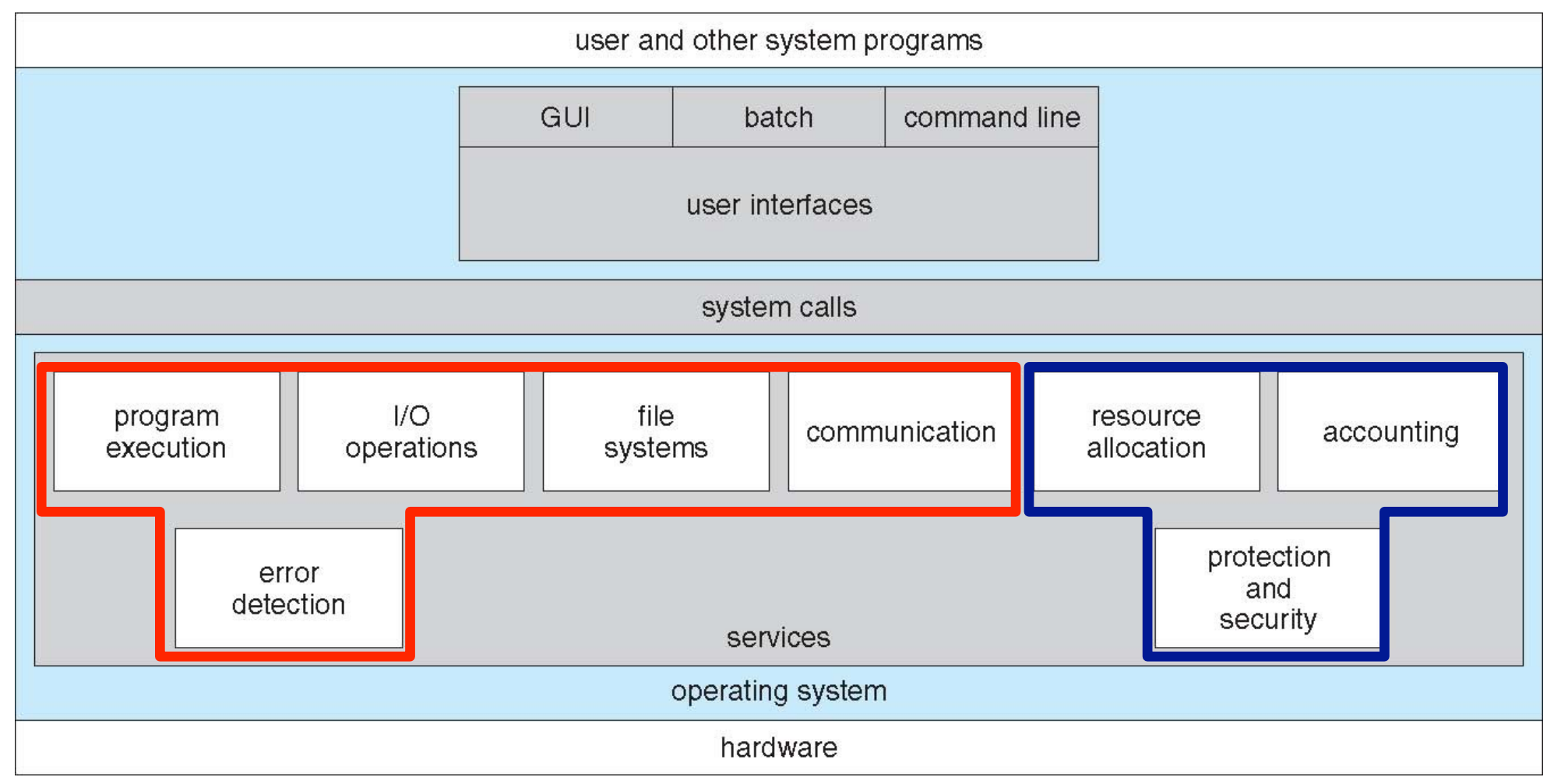
-
红色部分是 helpful to user, 蓝色部分是 better efficiency/operation.
-
User Operating System Interface
- CLI: Command Line Interface, shells
- GUI: user-friendly
- Touchscreen Interfaces
- Application Programming Interface(API)
System Calls¶
不同系统架构调用system call的方式
- x86-32: int
- -64: syscall
- arm64: svc
- EL0 User
- EL1 Kernel
- EL2 Hypervisor
- EL3 SM Secure Monitor
- 0->1: svc
- 1->2: hvc
- 2->3: smc
- risc-v: ecall
- Programming interface to the services provided by the OS
- Typically written in a high-level language
- Mostly accessed by API(Application Programming Interface)
printf&write¶
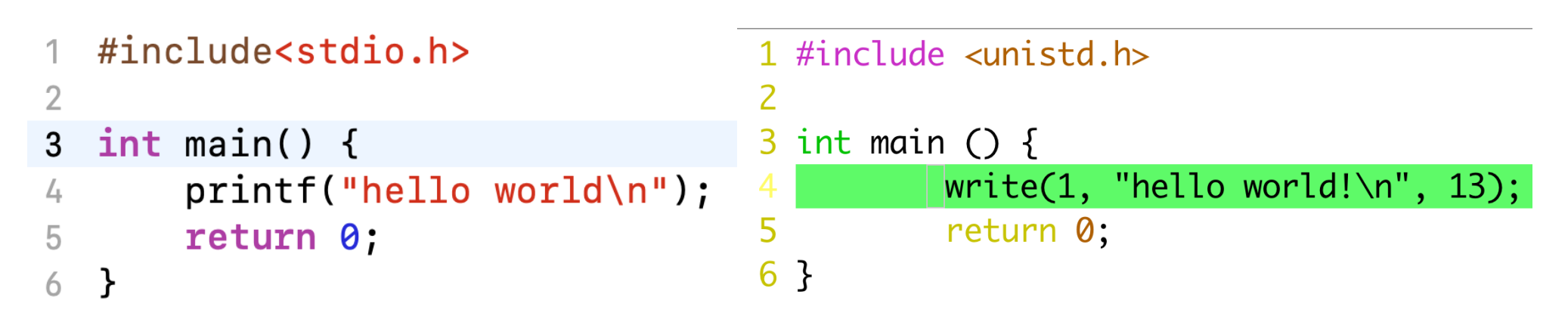
unist: Unix Standard
printf 是 write (system call) 的一个 wrapper。这里我们可以通过 man 2 write 查看系统调用的用法(2 表示查询系统调用)
fd=1表示标准输出, fd指file descriptorbuf是要输出的内容,指向hello world\n这个字符串首地址。count=13是要输出的字节数(包含了\n)
write系统调用号为1
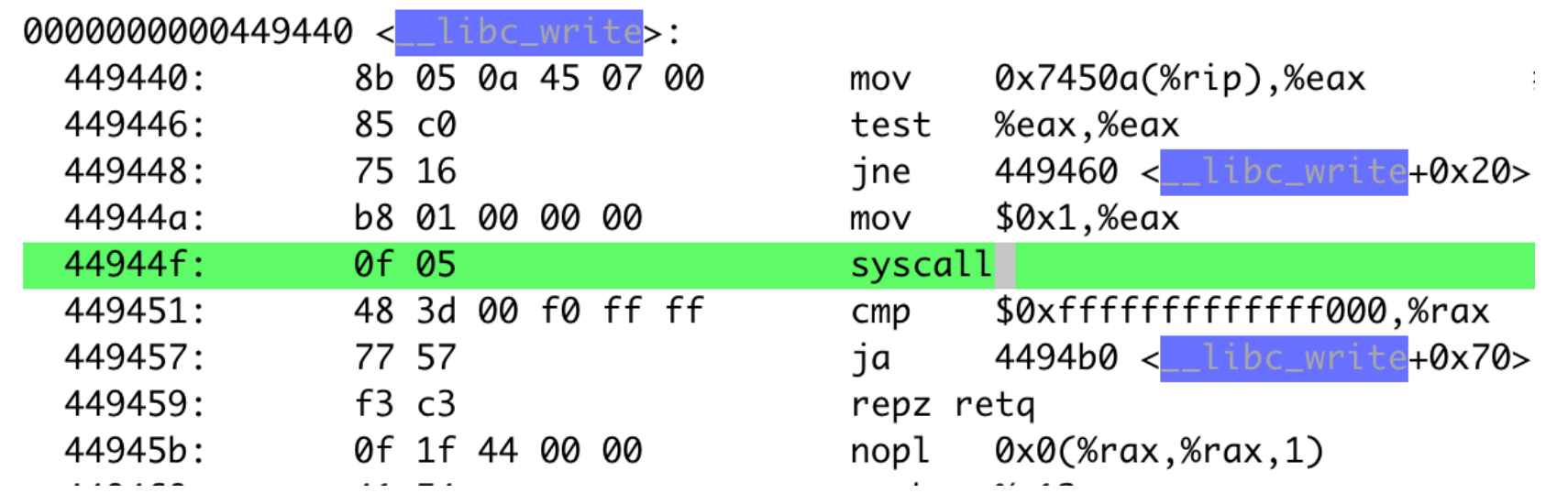
objdump -d 翻译成汇编可以看到,main 里会调用 __libc_write。

在 __libc_write 里会将 1(系统调用号)挪到寄存器 %eax 里随后调用了 syscall 指令,跳到 kernel space,并且切换 mode。
Linux0.11
之后在Kernel Space
kernel_entry被调用,save所有user space寄存器- call
writesyscall handler: 从syscall_table中获取函数指针 syscall_table为array,其index为系统调用号,- 写完后调用
ret_to_user,恢复寄存器,返回到user
用户不需要知道系统调用的具体实现
The Hidden Syscall Table
需要通过 C 预处理得到宏展开的文件,
make *.i可以得到对应的.i文件拷贝文件需要调用的syscall
strace¶
strace: system call trace. e.g. strace cp main.c main 可以看到我们调用 cp main.c main 时,调用了哪些系统调用。可以用 strace 知道我们的程序调用了什么系统调用之后出问题。
time¶
time 可以输出 real, user, sys 的时间。(real 表示时钟的时间,后两个表示对应mode的时间)
有时 user 和 sys 是多进程同时进行,所以加起来的时间比时钟的时间长。
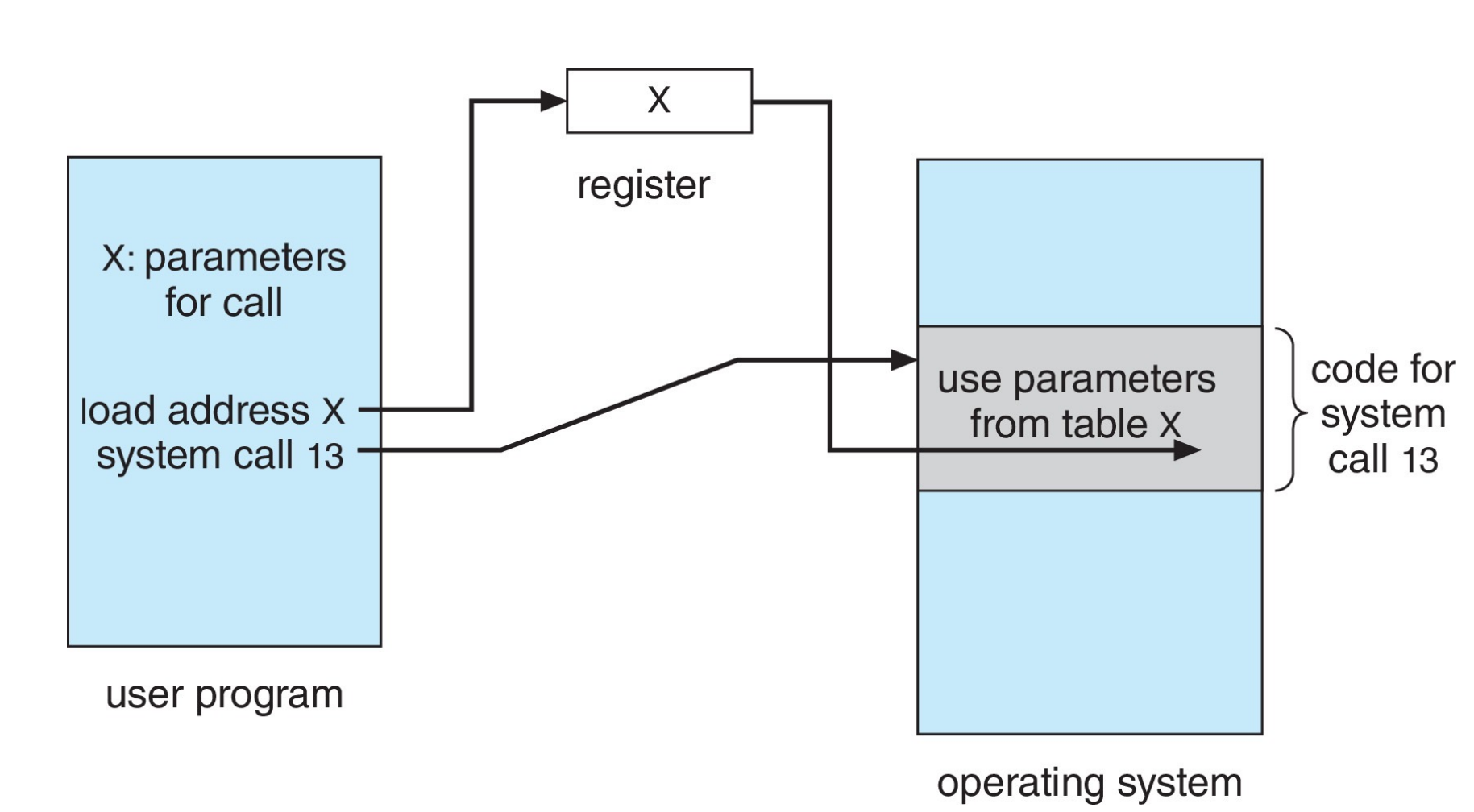
System Call Parameter Passing¶
直接放在寄存器里或把地址放在寄存器里,通过地址访问
或者把参数push到栈上,操作系统从栈上pop
Types of System Calls¶
- Process control
- create process, terminate process
- end, abort;
- load, execute
- get process attributes, set process attributes
- wait for time
- wait event, signal event
- allocate and free memory
- Dump memory if error 内存转储
- Debugger for determining bugs, single step execution
-
Locks for managing access to shared data between processes
-
File management
- Device management
- Information maintenance
- Communications
- create, delete communication connection
- send, receive messages if message passing model to host name or process name
- Shared-memory model create and gain access to memory regions
- transfer status information
-
attach and detach remote devices
-
Protection
Linkers and Loaders¶
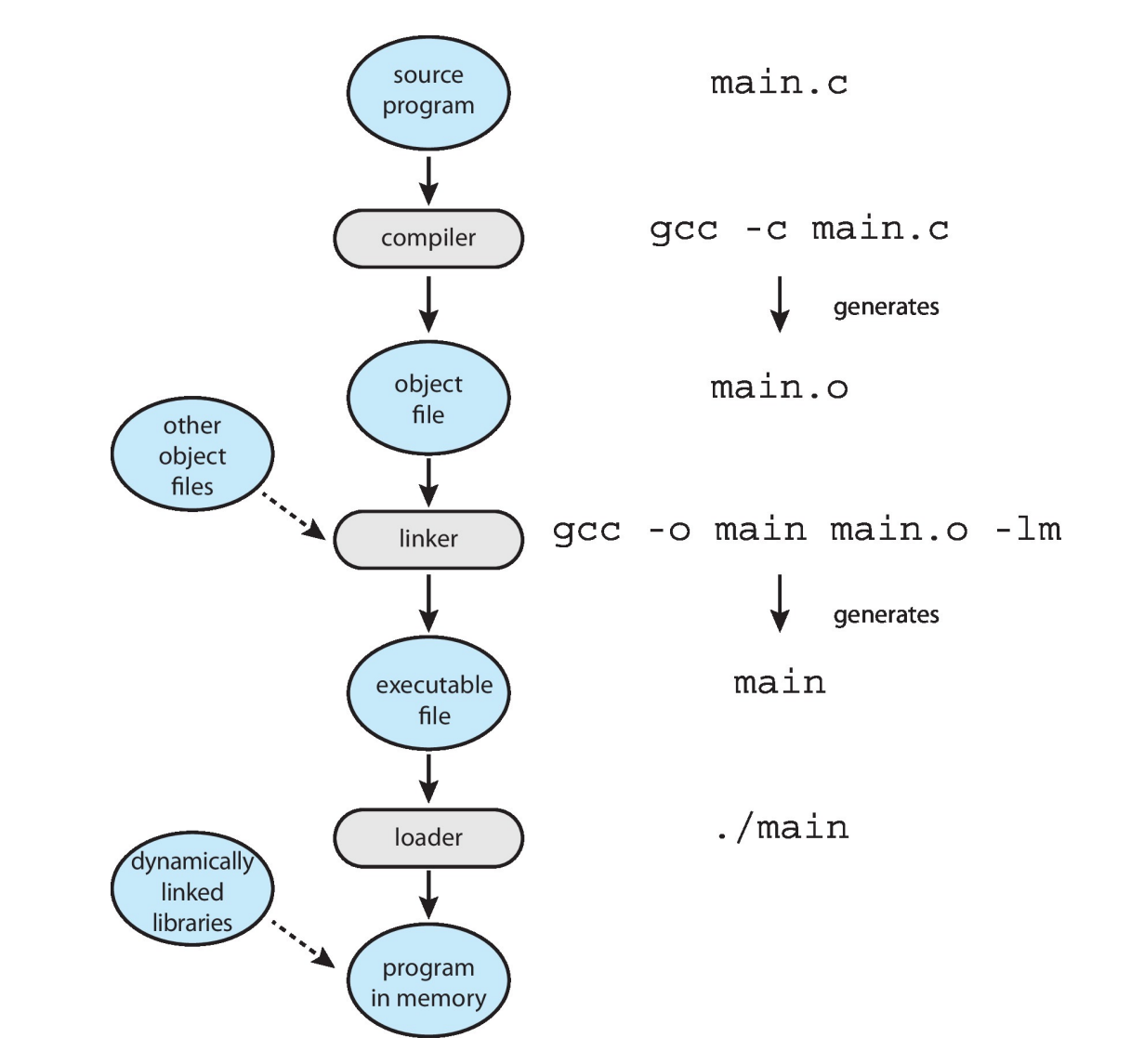
从 .c 文件到 .o 文件经过了下面的流程:
- 预处理
cpp main.c -o main.i - 编译
gcc -S main.i -o main.s - 汇编
as main.s -i main.o - Linker combines these into single binary executable file.
- Loader loads executable file into memory and starts execution.
- Modern general purpose systems don’t link libraries into executables.
- Rather, dynamically linked libraries (in Windows, DLLs) are loaded as needed
ELF binary basics¶

- Executable and Linkable Format - ELF
- Section header & Program header
一个给 Linker 用,一个给 Loader 用。 .text: code.rodata: initialized read-only data static const.data: initialized data static variable.bss: uninitialized data 全初始化为0,存储空间为0
readelf查看elf信息,包括每个段起始地址大小等信息readelf -S a.out
Linking¶
- static linking: 可移植性高,把所有的代码都放到一个二进制文件,大
- dynamic linking: Reuse libraries to reduce ELF file size 小
.interp段里存着loader的路径- loader resolves lib calls
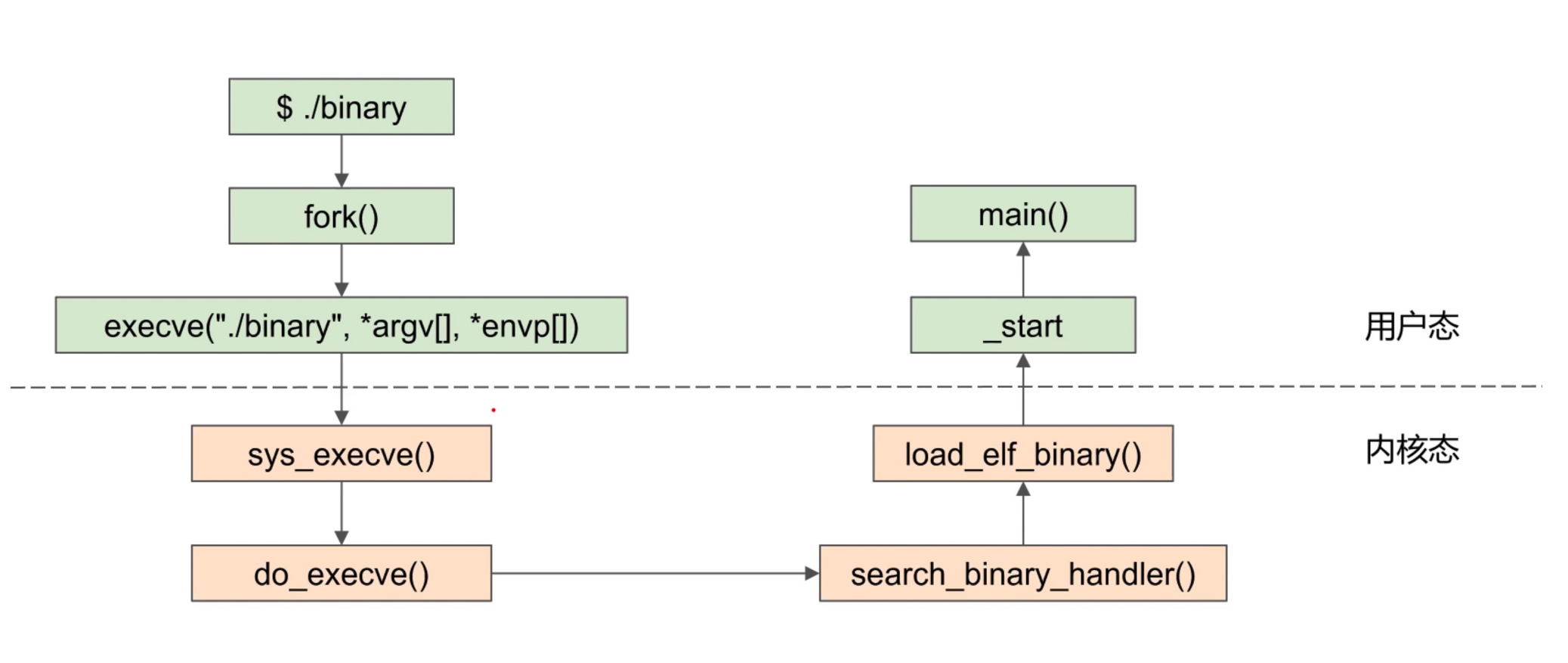
Running a binary¶
运行时的内存布局:

ELF section 被映射到内存里面的不同 segment。 注意区分堆和栈,分配数据时 stack 快,heap 慢。
- who setup ELF files mapping?
- Kernel
- exec syscall
- who setup stack and heap?
- Kernel
- exec syscall
- who setups libraries?
- Loader
- ld-xxx
Map¶
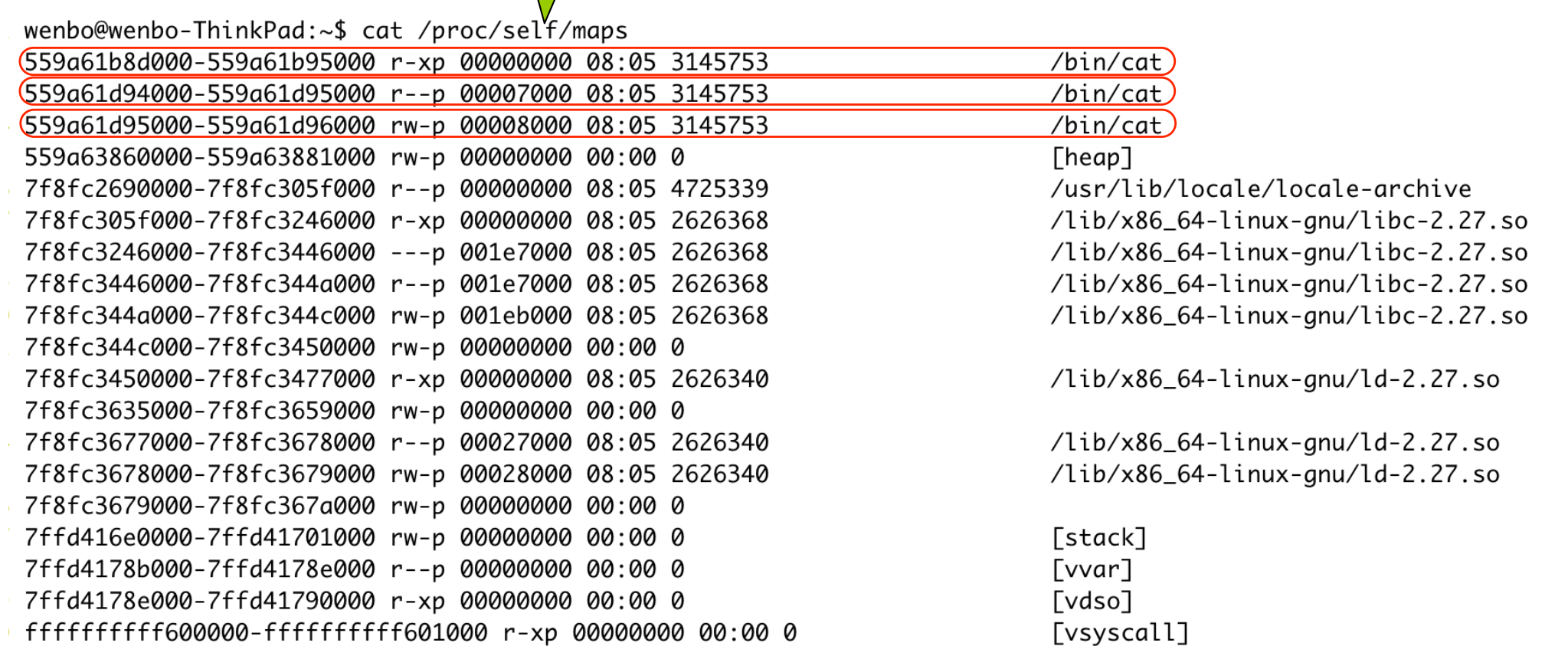
- text: r-xp
- r--p: rodatas
- rw-p: data
- .bss: uninitialized variables. 给一个全局变量不给值,早期编译器记录它在
.bss段里,但没有实际空间,映射到内存时就初始化为 0。 - heap/stack 匿名映射,没有一个文件支持。映射为可读可写。
Running a binary (Statically-linked)¶
首先我们通过 strace 查看运行静态链接文件过程中发生的系统调用。

execve执行对应路径的文件brk用于管理程序的数据段的末尾,通过改变堆的边界来分配或释放内存write执行程序里的printf功能
通过entry point address知道程序从哪一行开始

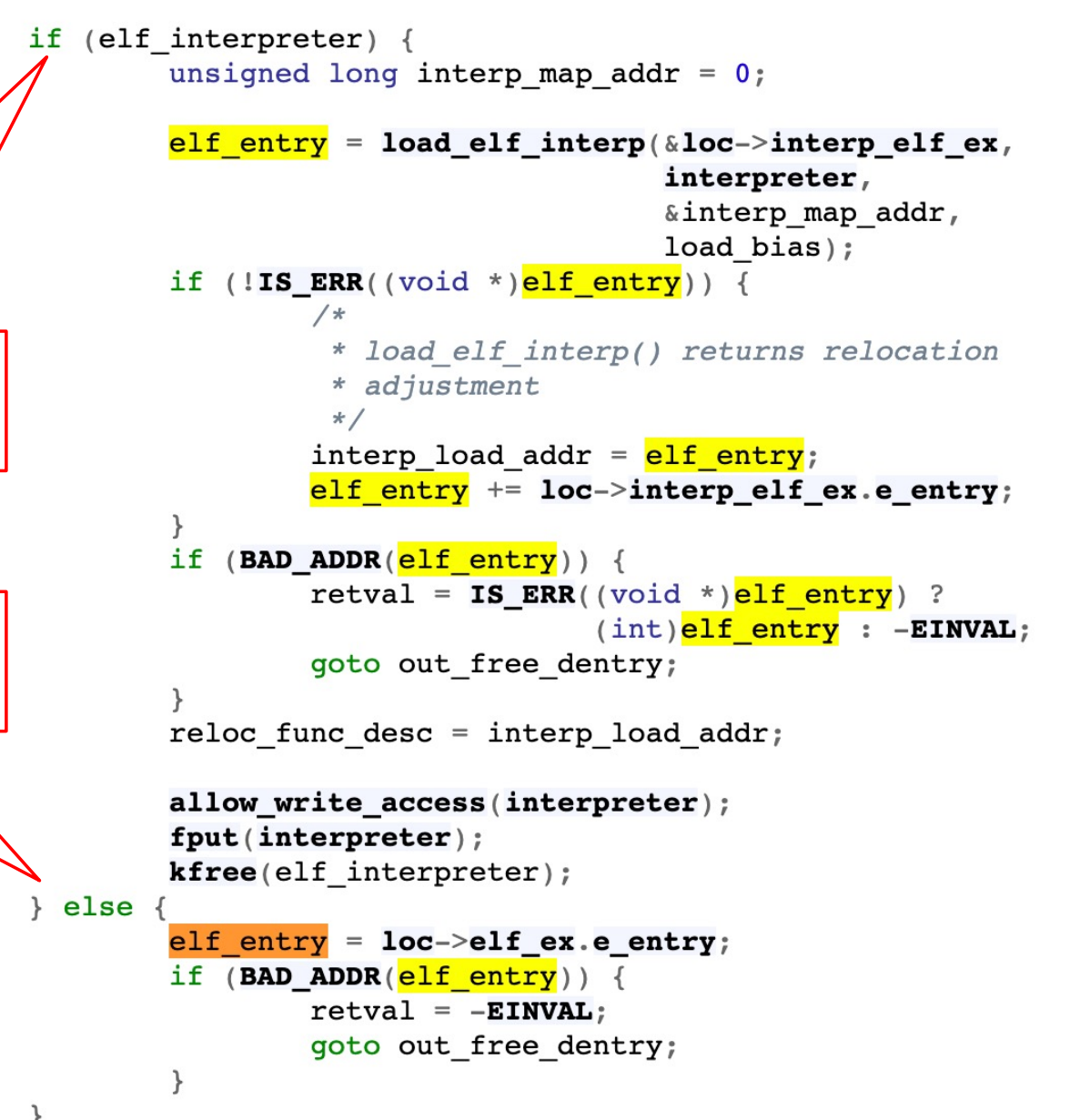
sys_execve() 里有 load_elf_binary 函数,从 ELF 头读地址到 elf_entry,把地址当作 regs->pc。然后调用 start_thread 函数。
ELF 里有 entry point address(通过 readelf -h)
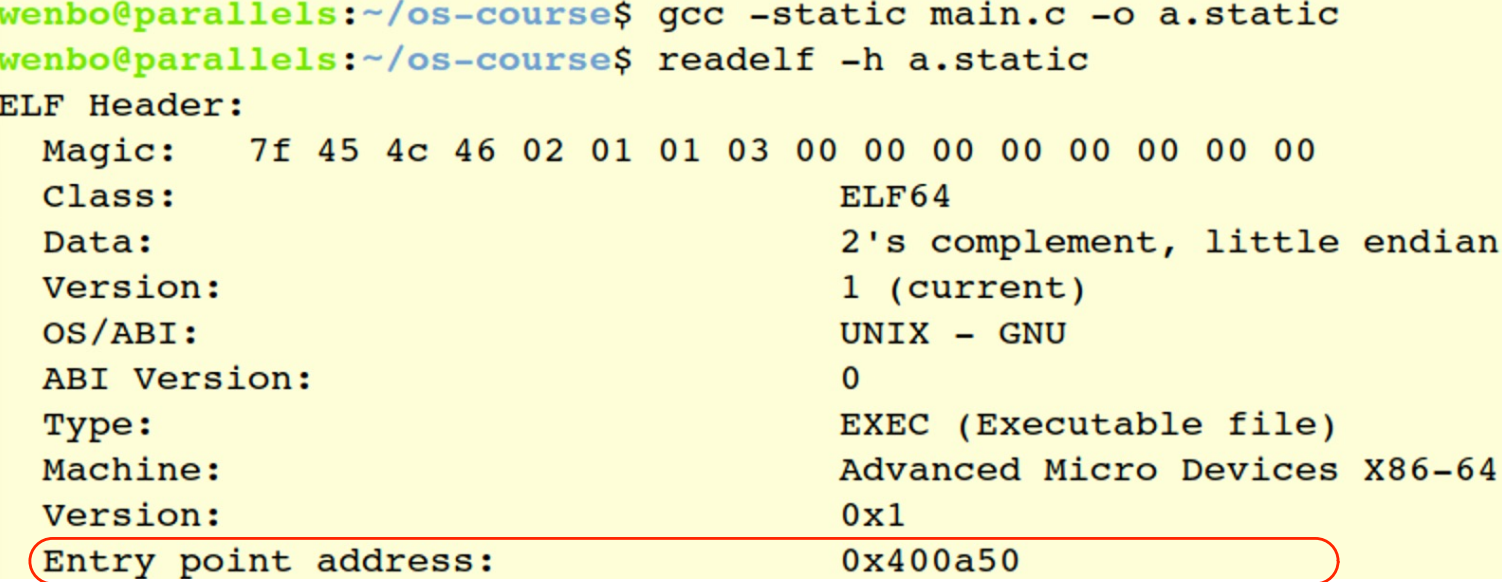
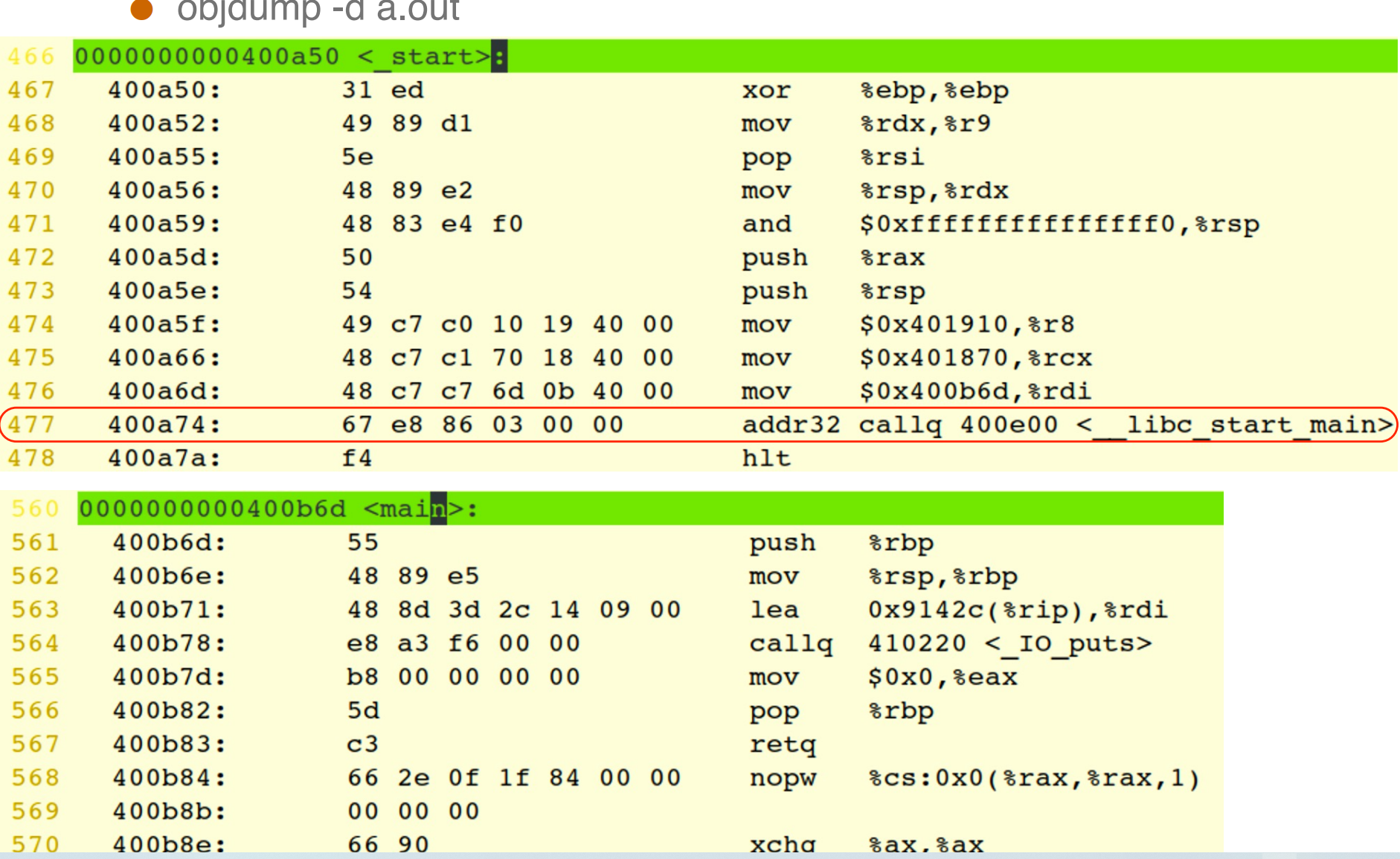
entry point address 不是 main() 的地址,而是 _start 的地址,里面会调用 __libc_start_main 函数,里面才调用 main() 函数。
_start 是在读取命令行参数并且传给 main。
cat /proc/pid/maps 里可以看到进程的内存映射。static 的条目更少,因为需要的东西已经打包到 a.static 内了,不需要外部的库。而 dynamic 需要外部的库。
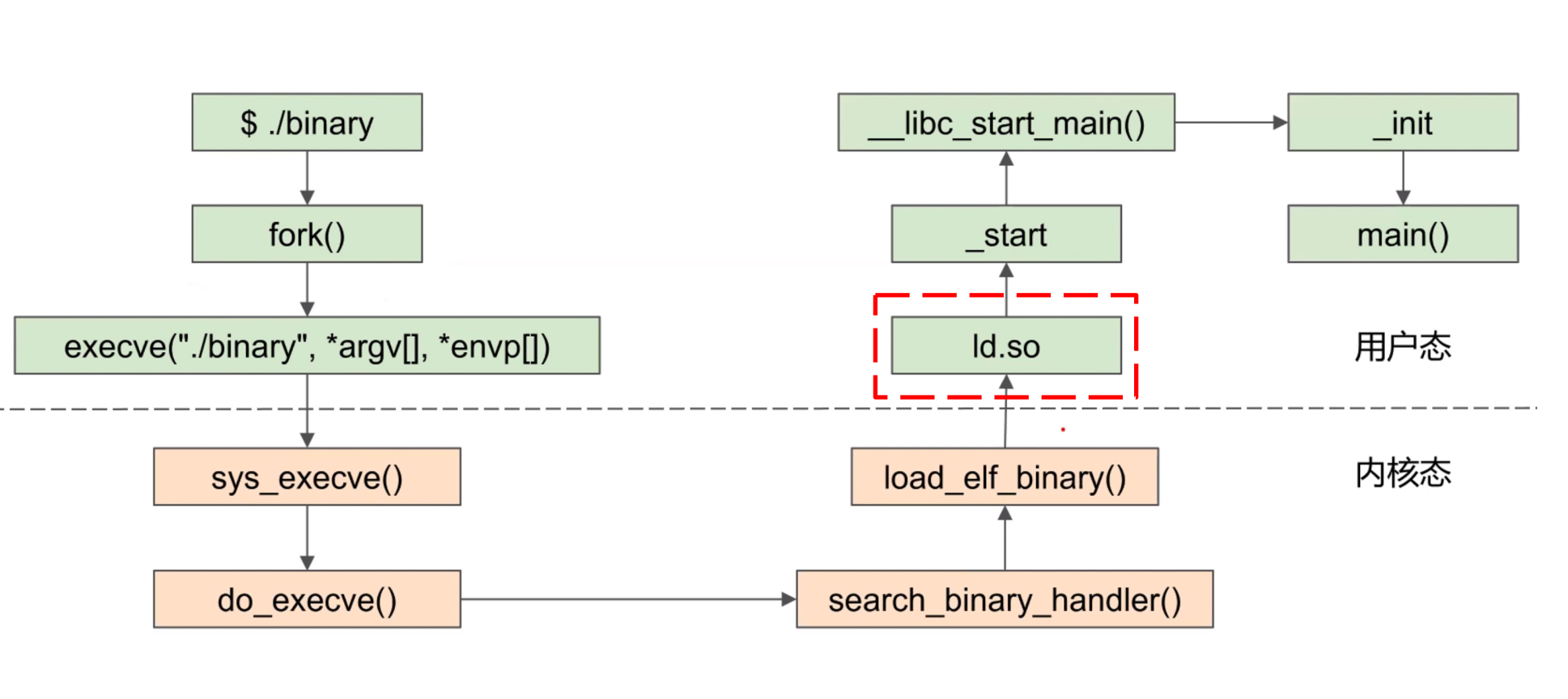
Running a binary (Dynamically-linked)¶
相比于静态链接,动态链接:
- 需要一个 loader。
- 动态链接的内存布局中条目更多。
- 动态链接的系统调用比静态的多。
- 动态链接的 entry point 的地址很小,也是对应
_start的地址,里面有些 symbol 还没有被解析。
类似地,我们先通过 strace 查看运行动态链接文件中使用了哪些系统调用。
可以看到相比于静态链接,多出来的系统都用都和 ld 有关,即 dynamic loader。

动态链接有 .interp 段,在 load_elf_binary 函数中会走另一个分支:entry point 会指向 loader 的地址。先加载loader
Why Applications are Operating System Specific¶
- 开发的软件不能直接跨平台调用,因为操作系统不同导致系统调用不同,下面的硬件也不同。
- 像 Java 开发的软件可以,因为有 JVM 提供了跨系统的平台。为每一个主流OS各写一个JVM
- Application Binary Interface (ABI) is architecture equivalent of API, defines how different components of binary code can interface for a given operating system on a given architecture, CPU, etc... Application Binary Interface (ABI) 更贴近硬件架构
Operating System Design and Implementation¶
- Policy vs Mechanism
- Policy: What will be done
- Mechanism: How to do it
- 应该把Policy和Mechanism分开, a very important principle
- Monolithic – Unix, Linux
- Linux System Structure

Layered Approach¶
The bottom layer (layer 0), is the hardware; the highest (layer N) is the user interface

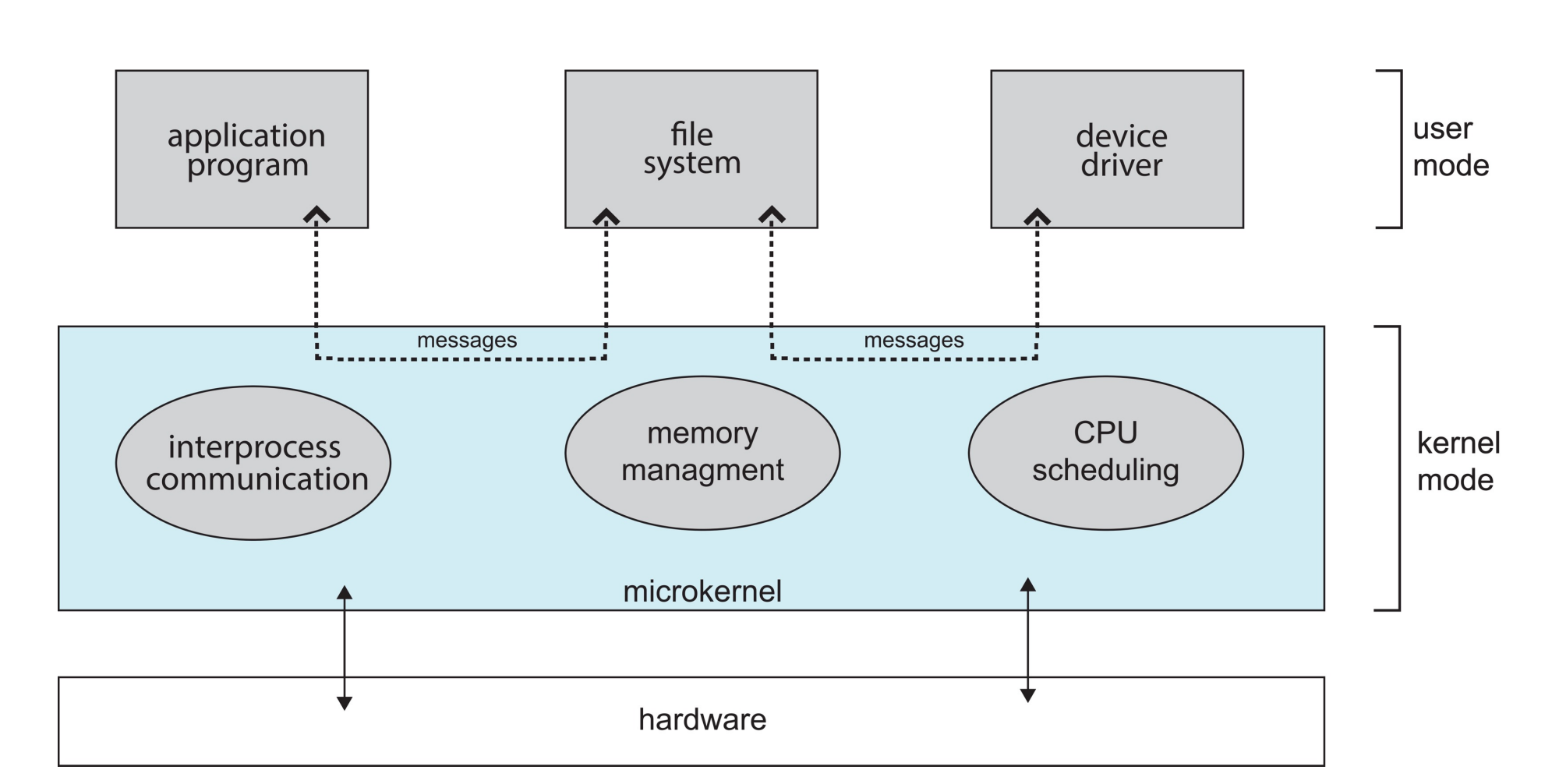
Microkernels¶
宏内核里放有很多 driver,而 driver 出问题,直接影响到 CPU 的 scheduler.
microkernel: Moves as much from the kernel into user space.
把 driver, file system... 都放到 user space,只留下最核心的东西在 kernel space.
- benefits:
- Easier to extend a microkernel
- Easier to port the operating system to new architectures
- More reliable (less code is running in kernel mode)
- More secure
- detriments:
- Performance overhead of user space to kernel space communication
Many modern operating systems implement loadable kernel modules (LKMs).
Modules¶
- Many modern operating systems implement loadable kernel modules (LKMs)
Hybrid Systems¶
Most modern operating systems are actually not one pure model

