Chapter 3 Combinational Logic Design¶
Part 1 Implementation Technology and Logic Design¶
分层设计¶
- 原子模块(Primitive Block):与门、或非、非门等等
-
分层设计:模块可重用性非常重要。先决条件:电路是规整(regularity)的
- 分层设计即将复杂问题模块化为若干层次,之后逐个解决
- 分为自顶向下和自底向上
- 前者从需求开始,后者从现有模块开始
-
出现在设计中的模块被称为这个模块的一个实例(instance),将它应用称为实例化(instantiation)
集成电路¶
又叫做芯片,分为以下等级
- SSI (small-scale integrated) 不到10个gate
- MSI(medium-\(\cdots\)) 10-100个gates
- LSI(large\(\cdots\))成百上千个gates
- VLSI(very large) 成千上亿个gates
技术参数¶
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| Fan-in | 一个门可用的输入 |
| Fan-out | 一个栅极输出驱动的标准负载数量 |
| Logic Levels | 被认为是高低电平的输入输出电压范围 |
| Noise Margin | 对外界噪声的容忍能力(具体来说是不会导致行为异变的最大噪声压值) |
| Cost for a gate | 继承电路的门成本 |
| Propagation Delay | 信号改变后从输入到输出所需的变化时间 |
| Power Dissipation | 电源输出能耗和门的能耗 |
- 扇入扇出:扇入描述了一个门能够接受的最多输入量,如一个四输入与非门的扇入就是 4;而扇出描述的则是一个门的输出(栅极输出)在不降低工作性能的情况下能够负载多少门,例如一个非门的输出能够同时负载 4 个非门并且都能正常工作,则其扇出为 4,其也能通过标准负载来定义。
-
所谓的标准负载,是衡量“负载”的一个“单位砝码”。其大小等于一个非门(逆变器)贡献的负载压力。
-
转换时间:转换时间分为\(t_{LH}\)(rise time)和\(t_{HL}\)(fall time)两个部分
- rise time 等于栅极输出从 \(V_{CC}\) 的 10% 升高到 90% 所需要的时间;
- fall time 等于栅极输出从 \(V_{CC}\)的 90% 降低到 10% 所需要的时间;
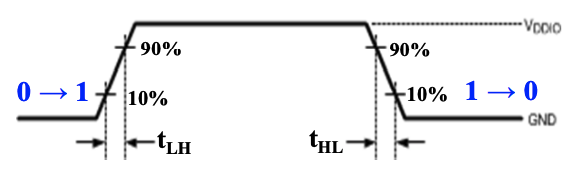
- 随着负载增加,转换时间也会增加(给电容充电的时间增加),而扇出定义中提到的“最大负载”,就是指它的转换时间不超过它预定的最大转换时间。

- 从左到右表示负载不断增加时,rise time 的变化趋势。
- 实际上,类似的,超出扇入后,门对输入的反应就太慢了。
工艺映射¶
形式上: 积之和形式使用与非门,和之积形式使用或非门
NAND Mapping Algorithm 与非门成本更低,延迟更低¶
-
Replace ANDs and ORs:

-
消除所有反相器对
-
Repeat the following pair of actions until there is at most one inverter between :
-
A circuit input or driving NAND gate output, and-
-
The attached NAND gate inputs.

-
NOR Mapping Algorithm¶
Similar to the NAND,first Replace ANDs and ORs

EN 使能¶
EN为0输出始终为0,EN为1时为对应表达式值
Part 2 Combinational Logic¶
Decoding 译码¶
- Decoding - the conversion of an n-bit input code to an m-bit output code with\(n\leqslant m\leqslant2^n\) such that each valid code word produces a unique output code
- Circuits that perform decoding are called decoders
- Here, functional blocks for decoding are called n-to-m line decoders, where \(m\leqslant2^n\), and generate \(2^n\) (or fewer) minterms for the n input variables
3-8 译码器¶

设计n输入译码器,不断二分,除不尽就剩下一个单独的,如上图3除2余1,因此我们使用1个4-2译码器和一个1-2-Line Decoder
通过译码器和OR可以组成任何组合逻辑电路
Decoder with Enable¶

由于2-4译码器只有一个输出为1,只有该门可以输出内容,因此可以将\(A_1,A_0\)组成的译码器当成EN,EN当成输入信号
带使能输入的译码器又被称为多路分配器
基于译码器的组合电路¶
当F最小项个数超过\(\overline{F}\)最小项个数,函数取反可以用更少最小项表示
BCD-to-Segment Decoder¶
- 共阳极与共阴极接法:


Encoding¶
-
Encoding - the opposite of decoding - the conversion of an m-bit input code to a \(n\)-bit output code with \(n < m< 2^n\) such that each valid code word produces a unique output code
-
An encoder has \(2^n\) (or fewer) input lines and \(n\) output lines which generate the binary code corresponding to the input values
-
传统编码器问题:如以下输出方程式对应编码器,若\(D_6,D_7\)同时为1,不能判断是\(A_2\)还是\(A_1\),即有不确定性

- 优先编码器(Priority Encoder)
位数越高优先级越高。增加一个单独输出V表示至少有一个输入为0以与\(D_0=1\)区分
- One encoder that can accept all possible combinations of input values and produce a meaningful result is a priority encoder.
- Among the 1s that appear, it selects the most significant input position (or the least significant input position) containing a 1 and responds with the corresponding binary code for that position.
- example:
- Priority encoder with 5 inputs (D4, D3, D2, D1, D0) - highest priority to most significant 1 present - Code outputs A2, A1, A0 and V where V indicates at least one 1 present.
- <div align="center"><img src="https://pixe1ran9e.oss-cn-hangzhou.aliyuncs.com/image-20231026111647111.png" alt="image-20231026111647111" style="zoom:50%;" /></div>
- Xs in input part of table represent 0 or 1; thus table entries correspond to product terms instead of minterms. The column on the left shows that all 32 minterms are present in the product terms in the table
- Xs 在输出列表示无关情况不同
Selecting¶
- Selecting of data or information is a critical function in digital systems and computers
- Logic circuits that perform selecting are called multiplexers
- Selecting can also be done by three-state logic or transmission gates
Multiplexer 多路复用器 MUX¶
- A multiplexer selects information from an input line and directs the information to an output line
- typical multiplexer has n control inputs (\(S_{n-1}, … S_0\)) called selection inputs, \(2^n\) information inputs (\(I_{2^n - 1}, … I_0\)), and one output \(Y\)
- A multiplexer can be designed to have m information inputs with \(m < 2^n\) as well as n selection inputs

2-to-1-Line Multiplexer¶
-
The single selection variable S has two values:
- S = 0 selects input \(I_0\)
- S = 1 selects input \(I_1\)
-
The equation:\(Y =\overline{S}I_0 + SI_1\)
-
The circuit:

Multiplexer Width Expansion(选择多位)¶
example:4-to-1-line quad multiplexer¶

Other Selection Implementations¶
- Three-state logic in place of AND-OR。 Gate input cost = 18

- Distributing the decoding across the three-state drivers(分层选择) Gate input cost = 14

- 基于传输门的

Combinational Logic Implementation- Multiplexer Approach 1¶

查找表
Combinational Logic Implementation - Multiplexer Approach 2¶


Part 3 Arithmetic functions¶
Function Block¶
Half-Adder¶
两输入两输出

- \(S\)为\(X\oplus Y,\)\(C\)为\(XY\)

- 常见两种电路实现

Full-Adder¶
全加器即考虑上一位的进位,即\(Z\)or\(C_i\)
S=\(\overline{C_i}(A\oplus B)+C_i(\overline{A\oplus B})\)

The term \(X\cdot Y\) is carry generate,\(X\oplus Y\) is carry propagate

- Ripple-Carry Binary Adder:需要延时 行波进位加法器

- Group Carry Lookahead Logic 超前进位加法器




每次使用上一块的进位结果,每一次进位结果延迟为3
Unsigned Subtraction¶

Complements 补码¶
- Diminished Radix Complement of N: defined as \((r^n-1)-N\) ,known as 反码 \(1's\) complement
- Radix Complement: defined as \(r^n-N\) \(2's\) complement
- 补码:对n位二进制数,相当于第一位\(a_{n-1}\)代表\(-2^{n-1}\),后续每位都代表\(2^k\)

即M-N时,减数N先求补码\(2^n-N\),然后\(M+(2^n-N)\),若产生进位1,说明够减,对应值即为答案;若进位为0,说明不够减,则对结果取补码并加负号
有符号减法¶
- 设加法为0,减法为1,正数第一位0,负数第一位1,那么对减数第一位,符号,被减数第一位构成的序列,若有偶数个0,在没有溢出情况下则可以转化为同号相加
- 若被加数与被减数为负,则取对应补码(不改变符号位),之后若是加法则正常进行,减法则类似地对减数取补

S=1为减法器,S=0为加法器
溢出¶
同号相加、异号相减时可能会出现溢出
- 判断溢出:\(V=C_n\oplus C_{n-1}\),即\(C_n\)与\(C_{n-1}\)符号一致则不溢出,否则溢出
两个正数相加,\(C_n\)一定是0,溢出只可能是\(C_{n-1}\)为1
两个负数相加,\(C_n\)一定是1,若不溢出\(C_{n-1}\)需要为1
-
无符号数溢出:两个首位都是1
-
有符号数:同号时有可能溢出
常数除法、乘法¶
对于2的幂次可以通过移位得到结果,对于非2幂次可以常数加法和2的幂次乘除相结合得到结果。
如\(3x=2^1x+2^0x\),即\(x[31:0]=\{x[30:0],1'b0\}+x[31:0]\).
压缩、递增、递减¶
- 压缩:针对特定应用时简化已有模块,如递增递减等

零填充与符号扩展¶
- 增加输入位数:在高位添加或在低位添加,前者适用于加减,后者适用于低精度乘法